Peptide Hydrogel for Sustained Release of Recombinant Human Bone Morphogenetic Protein-2 In Vitro
- PMID: 39728169
- PMCID: PMC11677606
- DOI: 10.3390/jfb15120369
Peptide Hydrogel for Sustained Release of Recombinant Human Bone Morphogenetic Protein-2 In Vitro
Abstract
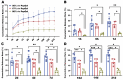
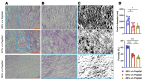
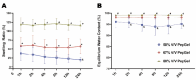
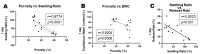
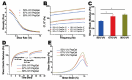
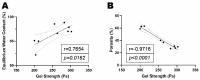
This study aimed to investigate the impact of varying the formulation of a specific peptide hydrogel (PepGel) on the release kinetics of rhBMP-2 in vitro. Three PepGel formulations were assessed: (1) 50% v/v (peptides volume/total volume) PepGel, where synthetic peptides were mixed with crosslinking reagents and rhBMP-2 solution; (2) 67% v/v PepGel; (3) 80% v/v PepGel. Each sample was loaded with 12 µg of rhBMP-2 and incubated in PBS. Released rhBMP-2 was quantified by ELISA at 1 h, 6 h, and 1, 2, 4, 7, 10, 14, and 21 days. To explore how PepGel formulations influence rhBMP-2 release, the gel porosities, swelling ratios, and mechanical properties of the three PepGel formulations were quantitatively analyzed. The results showed that rhBMP-2 encapsulated with 50% v/v PepGel exhibited a sustained release over the 21-day experiment, while the 67% and 80% v/v PepGels demonstrated significantly lower rhBMP-2 release rates compared to the 50% formulation after day 7. Higher histological porosity of PepGel was significantly correlated with increased rhBMP-2 release rates. Conversely, the swelling ratio and elastic modulus of the 50% v/v PepGel were significantly lower than that of the 67% and 80% v/v formulations. In conclusion, this study indicates that varying the formulation of crosslinked PepGel can control rhBMP-2 release rates in vitro by modulating gel porosity, swelling ratio, and mechanical properties. Encapsulation with 50% v/v PepGel offers a sustained rhBMP-2 release pattern in vitro; if replicated in vivo, this could mitigate the adverse effects associated with burst release of rhBMP-2 in clinical applications.
Keywords: biomaterials; bone morphogenetic protein; controlled release; drug delivery; peptide hydrogel.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Controlled release of BSA-linked cisplatin through a PepGel self-assembling peptide nanofiber hydrogel scaffold.Amino Acids. 2017 Dec;49(12):2015-2021. doi: 10.1007/s00726-017-2444-z. Epub 2017 Jun 12. Amino Acids. 2017. PMID: 28603803
-
The influence of covalently linked and free polyethylene glycol on the structural and release properties of rhBMP-2 loaded microspheres.J Control Release. 2010 Oct 1;147(1):92-100. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2010.06.021. Epub 2010 Jul 29. J Control Release. 2010. PMID: 20603166
-
[Preparation and property of recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2 loaded hydrogel nanospheres and their biological effects on the proliferation and differentiation of bone mesenchymal stem cells].Shanghai Kou Qiang Yi Xue. 2005 Oct;14(5):485-9. Shanghai Kou Qiang Yi Xue. 2005. PMID: 16288327 Chinese.
-
Bone regeneration using photocrosslinked hydrogel incorporating rhBMP-2 loaded 2-N, 6-O-sulfated chitosan nanoparticles.Biomaterials. 2014 Mar;35(9):2730-42. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2013.12.028. Epub 2014 Jan 15. Biomaterials. 2014. PMID: 24438908
-
Sintered porous Ti6Al4V scaffolds incorporated with recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2 microspheres and thermosensitive hydrogels can enhance bone regeneration.RSC Adv. 2019 Jan 11;9(3):1541-1550. doi: 10.1039/c8ra10200g. eCollection 2019 Jan 9. RSC Adv. 2019. PMID: 35518032 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

