Improving the Anti-Tumor Effect of Indoleamine 2,3-Dioxygenase Inhibitor CY1-4 by CY1-4 Nano-Skeleton Drug Delivery System
- PMID: 39728172
- PMCID: PMC11676189
- DOI: 10.3390/jfb15120372
Improving the Anti-Tumor Effect of Indoleamine 2,3-Dioxygenase Inhibitor CY1-4 by CY1-4 Nano-Skeleton Drug Delivery System
Abstract
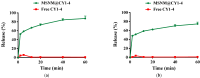
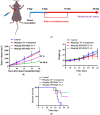
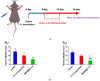
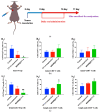
Background: CY1-4, 9-nitropyridine [2',3':4,5] pyrimido [1,2-α] indole -5,11- dione, is an indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO) inhibitor and a poorly water-soluble substance. It is very important to increase the solubility of CY1-4 to improve its bioavailability and therapeutic effect. In this study, the mesoporous silica nano-skeleton carrier material Sylysia was selected as the carrier to load CY1-4, and then the CY1-4 nano-skeleton drug delivery system (MSNM@CY1-4) was prepared by coating the hydrophilic polymer material Hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC) and the lipid material Distearoylphosphatidyl-ethanolamine-poly(ethylene glycol)2000 (DSPE-PEG2000) to improve the anti-tumor effect of CY1-4. Methods: The solubility and dissolution of MSNM@CY1-4 were investigated, and its bioavailability, anti-tumor efficacy, IDO inhibitory ability and immune mechanism were evaluated in vivo. Results: CY1-4 was loaded in MSNM@CY1-4 in an amorphous form, and MSNM@CY1-4 could significantly improve the solubility (up to about 200 times) and dissolution rate of CY1-4. In vivo studies showed that the oral bioavailability of CY1-4 in 20 mg/kg MSNM@CY1-4 was about 23.9-fold more than that in 50 mg/kg CY1-4 suspension. In B16F10 tumor-bearing mice, MSNM@CY1-4 significantly inhibited tumor growth, prolonged survival time, significantly inhibited IDO activity in blood and tumor tissues, and reduced Tregs in tumor tissues and tumor-draining lymph nodes to improve anti-tumor efficacy. Conclusions: The nano-skeleton drug delivery system (MSNM@CY1-4) constructed in this study is a potential drug delivery platform for improving the anti-tumor effect of oral poorly water-soluble CY1-4.
Keywords: MSNM@CY1-4; anti-tumor; anti-tumor immune; indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase; nano-skeleton.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Improving anti-tumor activity of sorafenib tosylate by lipid- and polymer-coated nanomatrix.Drug Deliv. 2017 Nov;24(1):270-277. doi: 10.1080/10717544.2016.1245371. Drug Deliv. 2017. PMID: 28165798 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancing Anti-Tumor Activity of Sorafenib Mesoporous Silica Nanomatrix in Metastatic Breast Tumor and Hepatocellular Carcinoma via the Co-Administration with Flufenamic Acid.Int J Nanomedicine. 2020 Mar 16;15:1809-1821. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S240436. eCollection 2020. Int J Nanomedicine. 2020. PMID: 32214813 Free PMC article.
-
Improving Solubility and Oral Bioavailability of Febuxostat by Polymer-Coated Nanomatrix.AAPS PharmSciTech. 2018 Feb;19(2):934-940. doi: 10.1208/s12249-017-0905-z. Epub 2017 Oct 27. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2018. PMID: 29079988
-
Indoleamine 2, 3-Dioxygenase: A Professional Immunomodulator and Its Potential Functions in Immune Related Diseases.Int Rev Immunol. 2022;41(3):346-363. doi: 10.1080/08830185.2020.1836176. Epub 2020 Oct 29. Int Rev Immunol. 2022. PMID: 33118843 Review.
-
Mesoporous silica materials: From physico-chemical properties to enhanced dissolution of poorly water-soluble drugs.J Control Release. 2017 Sep 28;262:329-347. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2017.07.047. Epub 2017 Aug 2. J Control Release. 2017. PMID: 28778479 Review.
References
-
- Kjeldsen J.W., Lorentzen C.L., Martinenaite E., Ellebaek E., Donia M., Holmstroem R.B., Klausen T.W., Madsen C.O., Ahmed S.M., Weis-Banke S.E., et al. A phase 1/2 trial of an immune-modulatory vaccine against IDO/PD-L1 in combination with nivolumab in metastatic melanoma. Nat. Med. 2021;27:2212–2223. doi: 10.1038/s41591-021-01544-x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Nandre R., Verma V., Gaur P., Patil V., Yang X., Ramlaoui Z., Shobaki N., Andersen M.H., Pedersen A.W., Zocca M.B., et al. IDO Vaccine Ablates Immune-Suppressive Myeloid Populations and Enhances Antitumor Effects Independent of Tumor Cell IDO Status. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2022;10:571–580. doi: 10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-21-0457. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

