Arrhythmia Detection in Atrioventricular, Single-Lead, Floating Atrial Dipole ICD Systems Compared with Conventional Single- and Dual-Chamber Defibrillators
- PMID: 39728276
- PMCID: PMC11677019
- DOI: 10.3390/jcdd11120386
Arrhythmia Detection in Atrioventricular, Single-Lead, Floating Atrial Dipole ICD Systems Compared with Conventional Single- and Dual-Chamber Defibrillators
Abstract
Background: An atrioventricular defibrillator system with a floating atrial dipole (VDD ICD) can provide atrial sensing by a single lead. Our aim was to compare the arrhythmia detection efficacy of VDD ICDs with conventional single- (VVI) and dual-chamber (DDD) defibrillators.
Methods: Data from consecutive patients undergoing ICD implantation were retrospectively analyzed. The primary endpoint was the incidence of device-detected, new-onset atrial arrhythmias, while secondary endpoints were sensing parameters, complication rates, incidence of appropriate/inappropriate ICD therapy, arrhythmic/heart failure-related hospitalizations, and all-cause mortality.
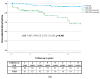
Results: A total of 256 patients (mean age 64 ± 12 years, male 75%, primary prophylaxis 28%, mean follow-up 3.7 ± 2.4 years) were included (VVI: 93, VDD: 94, DDD: 69). Atrial arrhythmia episodes were detected more frequently by VDD systems compared to VVI ICDs (aHR 7.087; 95% CI 2.371-21.183; p < 0.001), and at a rate similar to that of DDD ICDs (aHR 1.781; 95% CI 0.737-4.301; p = 0.200). The rate of inappropriate shocks was not different among the three ICD systems.
Conclusion: VDD devices revealed an advantage in atrial arrhythmia detection compared to VVI ICDs and were non-inferior to DDD systems. Their main indication may be closer monitoring in high-risk patients with atrial arrhythmias to help therapy optimization and not the improvement of tachycardia discrimination.
Keywords: ICD; VDD; atrial arrythmia detection; floating atrial sensing dipole; implantable cardioverter defibrillator; tachycardia discrimination.
Conflict of interest statement
T.S.-T. reports educational activity/advisory relationship with Biotronik, and until 2022, he was in educational/advisory/product development relationships with Ablacon Inc., Abbott, Acutus Medical, Biosense Webster, and Stereotaxis. M.V. reports educational activity and advisory relationship with Biotronik, and educational activity on behalf of KRKA, Medtronic, Novo Nordisk, and Pfizer. All other authors have nothing to disclose.
Figures

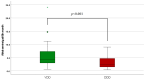
 : it represents an outliner value.
: it represents an outliner value.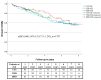
References
-
- Zeppenfeld K., Tfelt-Hansen J., de Riva M., Winkel B.G., Behr E.R., Blom N.A., Charron P., Corrado D., Dagres N., de Chillou C., et al. 2022 ESC Guidelines for the management of patients with ventricular arrhythmias and the prevention of sudden cardiac death. Eur. Heart J. 2022;43:3997–4126. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehac262. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Stroobandt R.X., Barold S.S., Sinnaeve A.F. Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillators Step by Step: An Illustrated Guide. John Wiley & Sons:; Hoboken, NJ, USA: 2011.
-
- Tzeis S., Gerstenfeld E.P., Kalman J., Saad E.B., Sepehri Shamloo A., Andrade J.G., Barbhaiya C.R., Baykaner T., Boveda S., Calkins H., et al. 2024 European Heart Rhythm Association/Heart Rhythm Society/Asia Pacific Heart Rhythm Society/Latin American Heart Rhythm Society expert consensus statement on catheter and surgical ablation of atrial fibrillation. EP Eur. 2024;26:euae043. doi: 10.1093/europace/euae043. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hindricks G., Theuns D.A., Bar-Lev D., Anguera I., Ayala Paredes F.A., Arnold M., Geller J.C., Merkely B., Dyrda K.M., Perings C., et al. Ability to remotely monitor atrial high-rate episodes using a single-chamber implantable cardioverter-defibrillator with a floating atrial sensing dipole. Europace. 2023;25:euad061. doi: 10.1093/europace/euad061. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Benz A.P., McIntyre W.F. Oral factor Xa inhibitors for stroke prevention in patients with device-detected atrial fibrillation—Recent evidence from the NOAH-AFNET 6 and ARTESiA trials. Cardiol. Hung. 2024;54:90–91. doi: 10.26430/CHUNGARICA.2024.54.2.90. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

