New Ground in Antifungal Discovery and Therapy for Invasive Fungal Infections: Innovations, Challenges, and Future Directions
- PMID: 39728367
- PMCID: PMC11678429
- DOI: 10.3390/jof10120871
New Ground in Antifungal Discovery and Therapy for Invasive Fungal Infections: Innovations, Challenges, and Future Directions
Abstract
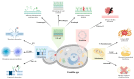
This review explores current advancements and challenges in antifungal therapies amid rising fungal infections, particularly in immunocompromised patients. We detail the limitations of existing antifungal classes-azoles, echinocandins, polyenes, and flucytosine-in managing systemic infections and the urgent need for alternative solutions. With the increasing incidence of resistance pathogens, such as Candida auris and Aspergillus fumigatus, we assess emerging antifungal agents, including Ibrexafungerp, T-2307, and N'-Phenylhydrazides, which target diverse fungal cell mechanisms. Innovations, such as nanoparticles, drug repurposing, and natural products, are also evaluated for their potential to improve efficacy and reduce resistance. We emphasize the importance of novel approaches to address the growing threat posed by fungal infections, particularly for patients with limited treatment options. Finally, we briefly examine the potential use of artificial intelligence (AI) in the development of new antifungal treatments, diagnoses, and resistance prediction, which provides powerful tools in the fight against fungal pathogens. Overall, we highlight the pressing need for continued research to advance antifungal treatments and improve outcomes for high-risk populations.
Keywords: antifungal therapy; drug resistance; fungal infections; nanoparticles; natural products; novel antifungals.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources