Energy-Resolved Mass Spectrometry and Mid-Infrared Spectroscopy for Purity Assessment of a Synthetic Peptide Cyclised by Intramolecular Huisgen Click Chemistry
- PMID: 39728617
- PMCID: PMC11676744
- DOI: 10.3390/mps7060097
Energy-Resolved Mass Spectrometry and Mid-Infrared Spectroscopy for Purity Assessment of a Synthetic Peptide Cyclised by Intramolecular Huisgen Click Chemistry
Abstract
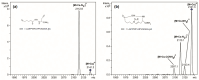
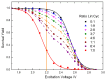
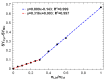
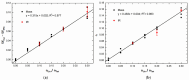
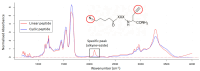
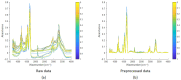
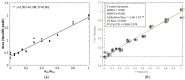
Cyclic peptides have higher stability and better properties as therapeutic agents than their linear peptide analogues. Consequently, intramolecular click chemistry is becoming an increasingly popular method for the synthesis of cyclic peptides from their isomeric linear peptides. However, assessing the purity of these cyclic peptides by mass spectrometry is a significant challenge, as the linear and cyclic peptides have identical masses. In this paper, we have evaluated the analytical capabilities of energy-resolved mass spectrometry (ER MS) and mid-infrared microscopy (IR) to address this challenge. On the one hand, mixtures of both peptides were subjected to collision-induced dissociation tandem mass spectrometry (CID MS/MS) experiments in an ion trap mass spectrometer at several excitation energies. Two different calibration models were used: a univariate model (at a single excitation voltage) and a multivariate model (using multiple excitation voltages). The multivariate model demonstrated slightly enhanced analytical performance, which can be attributed to more effective signal averaging when multiple excitation voltages are considered. On the other hand, IR microscopy was used for the quantification of the relative amount of linear peptide. This was achieved through univariate calibration, based on the absorbance of an alkyne band specific to the linear peptide, and through Partial Least Squares (PLS) multivariate calibration. The PLS calibration model demonstrated superior performance in comparison to univariate calibration, indicating that consideration of the full IR spectrum is preferable to focusing on the specific peak of the linear peptide. The advantage of IR microscopy is that it is linear across the entire working interval, from linear peptide molar ratios of 0 (equivalent to pure cyclic peptide) up to 1 (pure linear peptide). In contrast, the ER MS calibration models exhibited linearity only up to 0.3 linear peptide molar ratio. However, ER MS showed better performances in terms of the limit of detection, intermediate precision and the root-mean-square-error of calibration. Therefore, ER MS is the optimal choice for the detection and quantification of the lowest relative amounts of linear peptides.
Keywords: click chemistry; cyclic peptide; energy-resolved mass spectrometry; infrared microscopy; multivariate and univariate calibration; peptide isomers; quantification.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

