Reverse Osmosis Membrane Engineering: Multidirectional Analysis Using Bibliometric, Machine Learning, Data, and Text Mining Approaches
- PMID: 39728709
- PMCID: PMC11677704
- DOI: 10.3390/membranes14120259
Reverse Osmosis Membrane Engineering: Multidirectional Analysis Using Bibliometric, Machine Learning, Data, and Text Mining Approaches
Abstract
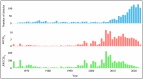
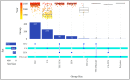
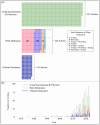
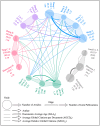
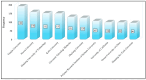
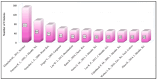
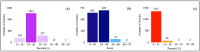
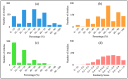
Membrane engineering is a complex field involving the development of the most suitable membrane process for specific purposes and dealing with the design and operation of membrane technologies. This study analyzed 1424 articles on reverse osmosis (RO) membrane engineering from the Scopus database to provide guidance for future studies. The results show that since the first article was published in 1964, the domain has gained popularity, especially since 2009. Thin-film composite (TFC) polymeric material has been the primary focus of RO membrane experts, with 550 articles published on this topic. The use of nanomaterials and polymers in membrane engineering is also high, with 821 articles. Common problems such as fouling, biofouling, and scaling have been the center of work dedication, with 324 articles published on these issues. Wang J. is the leader in the number of published articles (73), while Gao C. is the leader in other metrics. Journal of Membrane Science is the most preferred source for the publication of RO membrane engineering and related technologies. Author social networks analysis shows that there are five core clusters, and the dominant cluster have 4 researchers. The analysis of sentiment, subjectivity, and emotion indicates that abstracts are positively perceived, objectively written, and emotionally neutral.
Keywords: Biblioshiny; Flesch reading ease score; Google Gemini; emotion analysis; large language models; reading time score; reverse osmosis; technical term density.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Lin S., Elimelech M. Staged reverse osmosis operation: Configurations, energy efficiency, and application potential. Desalination. 2015;366:9–14. doi: 10.1016/j.desal.2015.02.043. - DOI
-
- Qasim M., Badrelzaman M., Darwish N.N., Darwish N.A., Hilal N. Reverse osmosis desalination: A state-of-the-art review. Desalination. 2019;459:59–104. doi: 10.1016/j.desal.2019.02.008. - DOI
-
- Khanzada N.K., Choi P.J., An A.K. Chapter 5—Hybrid forward/reverse osmosis (HFRO): An approach for optimized operation and sustainable resource recovery. In: An A., Tyagi V., Kumar M., Cetecioglu Z., editors. Clean Energy and Resource Recovery. Elsevier; Amsterdam, The Netherlands: 2022. pp. 69–94.
-
- Wu Y.-G., Jiang M.-Y., Zhao J., Cai Y.-J., Li X.-Z., Yang X., Jiang H., Sun Y.-X., Wei N.-J., Liu Y., et al. Polyelectrolyte-based antifouling and pH-responsive multilayer coatings for reverse osmosis membrane. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2023;679:132642. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfa.2023.132642. - DOI
-
- Guan K., Fang S., Zhou S., Fu W., Li Z., Gonzales R.R., Xu P., Mai Z., Hu M., Zhang P., et al. Thin film composite membrane with improved permeance for reverse osmosis and organic solvent reverse osmosis. J. Membr. Sci. 2023;688:122104. doi: 10.1016/j.memsci.2023.122104. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

