Ergogenic and Sympathomimetic Effects of Yohimbine: A Review
- PMID: 39728757
- PMCID: PMC11677475
- DOI: 10.3390/neurolint16060131
Ergogenic and Sympathomimetic Effects of Yohimbine: A Review
Abstract
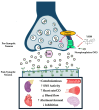
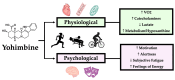
The purpose of this review is to compile and discuss available evidence in humans on the efficacy of YHM supplementation on performance in different exercise modalities. Yohimbine (YHM) is a naturally occurring alkaloid that induces increases in sympathetic nervous system (SNS) activation effectively initiating "fight or flight" responses. In supplement form, YHM is commonly sold as an isolated product or combined into multi-ingredient exercise supplements and is widely consumed in fitness settings despite the lack of empirical support until recently. YHM primarily acts as an α2-adrenergic receptor antagonist effectively increasing norepinephrine release from sympathetic neurons. YHM has been implicated in improving or altering cardiovascular function, blood flow, lactate metabolism, and muscle function. Emerging evidence has suggested that YHM may have the potential to improve performance in a wide range of exercise modes including endurance, sprint, and resistance exercise. Performance enhancement with YHM is mediated by mechanistic underpinnings of physiological and psychological alterations to exercise responses including increased sympathetic activation, adaptive hemodynamic changes, increased alertness, and decreased fatigue. However, YHM use is not without risk as it has high interindividual variability in bioavailability, can be deceptively potent, lacks widely accepted dosing recommendations, and, when taken in large doses, has been empirically documented to result in serious side effects. Despite this, the evidence presented in this review suggests low doses of YHM are tolerable and may serve as an ideal exercise training aid due to acute enhancement of physical performance. However, safety concerns remain outstanding and temperance should be used when using YHM and similar sympathomimetics.
Keywords: catecholamines; dietary supplement; stimulant; sympathetic nervous system.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Kotanska M., Marcinkowska M., Knutelska J., Zygmunt M., Sapa J. Yohimbine improves lipid and carbohydrate profiles without reduction in body weight in obese leptin-deficient ob/ob mice. J. Pre-Clin. Clin. Res. 2018;12:67–71. doi: 10.26444/jpccr/91404. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

