The Potential Influence of the Presence of Mycotoxins in Human Follicular Fluid on Reproductive Outcomes
- PMID: 39728767
- PMCID: PMC11728479
- DOI: 10.3390/toxins16120509
The Potential Influence of the Presence of Mycotoxins in Human Follicular Fluid on Reproductive Outcomes
Abstract
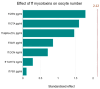
The effect of mycotoxin exposure on follicular fluid composition and reproductive outcomes in women undergoing in vitro fertilisation (IVF) was investigated in this study. Twenty-five patients were included, and follicular fluid and serum samples were analysed for various mycotoxins. Principal observations:1. Mycotoxin presence: All examined mycotoxins were detected in follicular fluid. Follicular fluid (ff) levels: Deoxynivalenol (DON), alfa-Zearalenol (α-ZOL), Zearalenone (ZEN), and total aflatoxin (AFs) were significantly higher in follicular fluid than in serum. 2. Follicular fluid and reproductive outcomes: A positive correlation was observed between the ratio of oocytes to total follicles and the follicular Fumonisin B1 (FB1) levels. Multiple linear regression analysis revealed a significant relationship between DON and T-2/HT-2 toxins (T2/HT2) levels in the follicular fluid. 3. Hormone levels: Follicular 17-beta estradiol (E2) and progesterone (P4) levels were higher than the serum levels. Follicular P4 correlated with serum P4 and Anti-Müllerian hormone (AMH) levels. In contrast, follicular E2 did not correlate with plasma E2 levels. 4. Mycotoxin-hormone interactions: A positive correlation was observed between follicular P4 and T2/HT2 toxin levels, whereas a negative correlation was found between ffE2 and ffT2/HT2, and a positive correlation was found between ZEN and E2. Conclusion: This study elucidated the presence of various mycotoxins in the follicular fluid and their potential influence on reproductive outcomes. Further research is warranted to clarify the specific mechanisms underlying these effects and develop strategies for detecting mycotoxin exposure in women undergoing IVF.
Keywords: IVF; P4); anti-Müllerian hormone (AMH); ff steroids (E2; follicular fluid (ff) mycotoxins.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Anti-Müllerian hormone and progesterone levels in human follicular fluid are predictors of embryonic development.Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2019 Jun 19;17(1):47. doi: 10.1186/s12958-019-0492-9. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2019. PMID: 31217014 Free PMC article.
-
Gonadotrophin stimulation for in vitro fertilization significantly alters the hormone milieu in follicular fluid: a comparative study between natural cycle IVF and conventional IVF.Hum Reprod. 2014 May;29(5):1049-57. doi: 10.1093/humrep/deu044. Epub 2014 Mar 6. Hum Reprod. 2014. PMID: 24608520
-
Follicular fluid anti-Müllerian hormone (AMH) concentrations and outcomes of in vitro fertilization cycles with fresh embryo transfer among women at a fertility center.J Assist Reprod Genet. 2020 Nov;37(11):2757-2766. doi: 10.1007/s10815-020-01956-7. Epub 2020 Oct 6. J Assist Reprod Genet. 2020. PMID: 33025399 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-Müllerian hormone concentrations in the follicular fluid of the preovulatory follicle are predictive of the implantation potential of the ensuing embryo obtained by in vitro fertilization.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2007 May;92(5):1796-802. doi: 10.1210/jc.2006-1053. Epub 2007 Feb 27. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2007. PMID: 17327387
-
The impact of follicular fluid phthalate metabolites on the ovarian reserve and ovarian function in Indian women undergoing intracytoplasmic sperm injection.F S Sci. 2024 May;5(2):107-120. doi: 10.1016/j.xfss.2023.11.001. Epub 2024 Jan 12. F S Sci. 2024. PMID: 38219085
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

