A Multi-Enzyme Complex That Mitigates Hepatotoxicity, Improves Egg Production and Quality, and Enhances Gut and Liver Health in Laying Hens Exposed to Trace Aflatoxin B1
- PMID: 39728775
- PMCID: PMC11728630
- DOI: 10.3390/toxins16120517
A Multi-Enzyme Complex That Mitigates Hepatotoxicity, Improves Egg Production and Quality, and Enhances Gut and Liver Health in Laying Hens Exposed to Trace Aflatoxin B1
Abstract
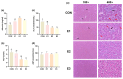
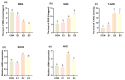
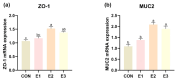
Aflatoxin B1 is a prevalent secondary hazardous metabolite generated by fungus present in feed ingredients and the surrounding environment: enzymes are currently being recognized as an efficient and promising approach to reducing the associated risks. The objective of this study was to assess the effects of varying doses of enzyme complexes on several parameters in laying hens that were exposed to aflatoxin. During an 8-week experiment, a total of 288 Yukou Jingfen No.6 laying hens were placed into four groups. These groups included a group treated with toxins (CON group) and groups supplemented with compound enzyme complexes at doses of 250 g/t (E1 group), 500 g/t (E2 group), and 1000 g/t (E3 group). The E2 and E3 groups exhibited a statistically significant 2.6% increase in egg production rate compared to the CON group (p < 0.05). In addition, the E2 group showed significant improvements in both the feed-to-egg ratio and egg weight (p < 0.05). In addition, the E2 and E3 groups showed improved hutch unit and egg white height compared to the control group (p < 0.05). The E2 and E3 groups showed a substantial rise in liver health indicators, namely serum alanine transaminase (ALT) and alkaline phosphatase (ALP) activity. On the other hand, malondialdehyde (MDA) was lowered, and total superoxide dismutase (T-SOD) and total antioxidant capacity (T-AOC) were raised. These findings were statistically significant (p < 0.05). The E2 and E3 groups showed notable enhancements in intestinal morphology, as evidenced by a rise in villus height and a decrease in crypt depth in all segments of the intestine (p < 0.05). Furthermore, analysis of 16S rRNA sequencing revealed that these participants had a higher prevalence and variety of microorganisms in their gut microbiota. More precisely, there was a significant rise in the abundance of Bacteroidota and a decline in Firmicutes at the level of the phylum. In general, the inclusion of the enzyme complex had advantageous impacts on performance, egg quality, intestinal morphology, intestinal barrier function, and intestinal flora in laying hens. Our results indicate that toxin-degrading enzymes, when used as feed additives, play a significant role in mitigating AFB1 contamination in diets and improving the production performance of laying hens.
Keywords: AFB1; gut health; gut microbiota; liver damage; liver metabolites; production.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Effects of purple sweet potato polysaccharide on performance, egg quality characteristics, jejunal morphology, and gut microbiota of Hy-Line Brown laying hens.Poult Sci. 2024 Dec;103(12):104366. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2024.104366. Epub 2024 Sep 27. Poult Sci. 2024. PMID: 39413705 Free PMC article.
-
Mitigation Effects of Bentonite and Yeast Cell Wall Binders on AFB1, DON, and OTA Induced Changes in Laying Hen Performance, Egg Quality, and Health.Toxins (Basel). 2021 Feb 17;13(2):156. doi: 10.3390/toxins13020156. Toxins (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33671260 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of supplemented multicomponent mycotoxin detoxifying agent in laying hens fed aflatoxin B1 and T2-toxin contaminated feeds.Poult Sci. 2023 Aug;102(8):102795. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2023.102795. Epub 2023 May 23. Poult Sci. 2023. PMID: 37327744 Free PMC article.
-
Alpiniae oxyphyllae fructus improves production performance and egg quality of laying breeder hens by regulating reproductive hormones, antioxidant function, immunity and intestinal health.Poult Sci. 2024 Jun;103(6):103770. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2024.103770. Epub 2024 Apr 15. Poult Sci. 2024. PMID: 38652955 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Chinese gallnut tannic acid on growth performance, blood parameters, antioxidative status, intestinal histomorphology, and cecal microbial shedding in broilers challenged with aflatoxin B1.J Anim Sci. 2022 Apr 1;100(4):skac099. doi: 10.1093/jas/skac099. J Anim Sci. 2022. PMID: 35352127 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Effects of Dietary Supplementation Using Phytobiotics with Different Functional Properties on Expression of Immunity Genes, Intestinal Histology, Growth, and Meat Productivity of Broiler Chickens.Vet Sci. 2025 Mar 25;12(4):302. doi: 10.3390/vetsci12040302. Vet Sci. 2025. PMID: 40284804 Free PMC article.
-
The Efficacy of Two Mycotoxin Detoxifications on Laying Performance, Antioxidant Capacity, and Liver Damage of Laying Hens Fed Diet Naturally Contaminated with Low-Level Mycotoxins.Vet Sci. 2025 May 26;12(6):520. doi: 10.3390/vetsci12060520. Vet Sci. 2025. PMID: 40559757 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chen X., Ishfaq M., Wang J. Effects of Lactobacillus salivarius supplementation on the growth performance, liver function, meat quality, immune responses and Salmonella Pullorum infection resistance of broilers challenged with Aflatoxin B1. Poult. Sci. 2021;101:101651. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2021.101651. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Alm-Eldeen A.A., Basyony M.A., Elfiky N.K., Ghalwash M.M. Effect of the Egyptian propolis on the hepatic antioxidant defense and pro-apoptotic p53 and anti-apoptotic bcl2 expressions in aflatoxin B1 treated male mice. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017;87:247–255. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2016.12.084. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

