Treatment with OnabotulinumtoxinA for Oromandibular Dystonia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 39728804
- PMCID: PMC11679302
- DOI: 10.3390/toxins16120546
Treatment with OnabotulinumtoxinA for Oromandibular Dystonia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
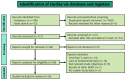
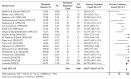
Oromandibular dystonia (OMD) is a focal dystonia characterized by contractions of the masticatory, lingual, and other muscles of the stomatognathic system. We conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis to elucidate the impact and safety of botulinum toxin in OMD. The eligibility criteria were full-length original articles that provided data evaluating the efficacy and adverse effects of onabotulinumtoxinA injections in patients with OMD. PubMed and Embase were searched for articles published before 31 May 2023. We analyzed cases that showed a favorable response (>0% improvement), moderate or greater response (>50% improvement), and adverse effects. A fixed-model meta-analysis of 26 studies involving 1103 patients revealed that an overall favorable effect of onabotulinumtoxinA injection was observed in 96.2% (95% confidence interval [CI], 95-97.5%, p < 0.00001) of patients, with significant heterogeneity (p < 0.00001, I2 = 85%). A moderate response (>50% improvement) was observed in 88.9% of patients (95% CI, 87-90.8%, p < 0.00001) with significant heterogeneity (p < 0.00001, I2 = 85%). Adverse effects were detected in 17.8% of patients, and the most common event was dysphagia (10.1%). Our systematic review found that onabotulinumtoxinA injection was effective, with a low rate of side effects. Further randomized controlled trials are required to clarify the evidence-based efficacy and adverse effects.
Keywords: adverse effect; botulinum toxin; botulinum toxin therapy; improvement; masticatory muscle; meta-analysis; onabotulinumtoxinA; oromandibular dystonia; safety; systematic review.
Conflict of interest statement
K.Y. declares no conflict of interest. R.K. declares the following financial interests/personal relationships which may be considered as potential competing interests: R.K. served as an advisor for Merz, IPSEN, Shionogi, Eisai, Teijin Pharma, and participated in speaker bureau activities for Teijin, GSK, and Eisai. A patent on A2NTX (WO, 2008/050866) is owned by Tokushima University and Shionogi Pharma, Osaka, Japan.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

