Impact of Ovarian Suspensory Ligament Rupture on Surgical Stress in Elective Ovariohysterectomy in Bitches
- PMID: 39728998
- PMCID: PMC11680349
- DOI: 10.3390/vetsci11120658
Impact of Ovarian Suspensory Ligament Rupture on Surgical Stress in Elective Ovariohysterectomy in Bitches
Abstract
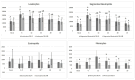
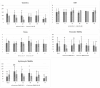
Ovariohysterectomy (OVH) is a common procedure in bitches, where ovarian suspensory ligament (OSL) rupture facilitates hemostasis but may also have adverse effects. Given the importance of minimizing the surgical stress response, this study aimed to evaluate the impact of OSL rupture in 20 healthy bitches undergoing elective open OVH; a celiotomy via the ventral midline was performed, and hemostasis achieved using bipolar coagulation, either with OSL rupture (OSL-R) or without (OSL-NR). Pain was assessed over 24 h post-surgery using the Visual Analogue Scale and the Short Form of the Glasgow Composite Measure Pain Scale. The physical parameters, complete blood count, glucose levels, erythrocyte sedimentation rate, and neutrophil oxidative and phagocytic functions were evaluated pre-surgery and at 6, 12, 24, and 48 h, as well as 10 days after. Oxidative metabolism was assessed through vitamin C and protein thiols, reduced glutathione, and thiobarbituric acid reactive substances. No differences in trans- and postoperative pain were observed between techniques, except for analgesic rescue rates. Differences were noted in the heart rate, total leukocyte count, segmented neutrophils, eosinophils, and monocytes. Both techniques resulted in low oxidative and phagocytic changes. Overall, OSL rupture appears to elicit a slightly more intense surgical stress response than the non-rupture technique.
Keywords: hemostasis; leukocyte response; oxidative stress markers; pain management.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Fransson B.A. Veterinary Surgery: Small Animal. Volume 2. Elsevier; St. Louis, MO, USA: 2018. Ovaries and Uterus; pp. 5694–5766.
-
- Hill L.N., Smeak D.D. Suspensory Ligament Rupture Technique during Ovariohysterectomy in Small Animals. Compend. Contin. Educ. Vet. 2010;32:E1–E7. quiz E8. - PubMed
-
- Dalmolin F., Rubio C.P., Furlanetto C.S., Steffens R., Hadi N.I.I.A., Da Silva A.D.L., Tomazi P., Antunes B.N., Elias F., Schmidt E.M.D.S., et al. Changes in Biomarkers of Inflammation and Oxidative Status in Dogs Subjected to Celiotomy or Video-Assisted Ovariohysterectomy. Vet. Sci. 2024;11:583. doi: 10.3390/vetsci11110583. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

