A Universal Multi-Epitope Vaccine Design Against Porcine Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome Virus via Bioinformatics and Immunoinformatics Approaches
- PMID: 39728999
- PMCID: PMC11680090
- DOI: 10.3390/vetsci11120659
A Universal Multi-Epitope Vaccine Design Against Porcine Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome Virus via Bioinformatics and Immunoinformatics Approaches
Abstract
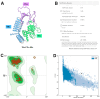
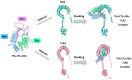
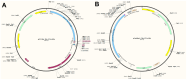
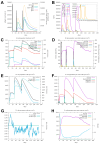
Porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus (PRRSV) causes reproductive disorders in sows and severe pneumonia in piglets, alongside immunosuppressive effects on the host. It poses a significant global threat to the swine industry, with no effective control measures currently available due to its complex pathogenesis and high variability. Conventional inactivated and attenuated vaccines provide inadequate protection and carry biosafety risks. In this study, we designed a universal multi-epitope peptide vaccine against PRRSV using bioinformatics and immunoinformatics approaches to address these limitations. By selecting sequences from seven representative PRRSV strains, we predicted highly conserved and immunogenic T cell (Th and CTL) epitopes across all encoded proteins. These were rationally concatenated with reported B cell neutralizing epitopes into a multi-epitope vaccine construct. We performed comprehensive assessments of the construct's physicochemical and biochemical properties, along with predictions and refinements of its secondary and tertiary structures. Molecular docking simulations with TLR2 and TLR4 revealed strong potential binding interactions. Immune simulations indicated that the multi-epitope vaccine could induce robust humoral and cellular immune responses. This study provides a scientific foundation for the development of safe and effective PRRSV subunit vaccines and offers new perspectives for designing vaccines against other viral diseases.
Keywords: PRRSV; bioinformatics; immunoinformatics; multi-epitope; universal vaccine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
In silico design of multi-epitope vaccine candidate based on structural proteins of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus.Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2025 Feb;280:110881. doi: 10.1016/j.vetimm.2025.110881. Epub 2025 Jan 5. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2025. PMID: 39847849
-
Epitope screening and vaccine molecule design of PRRSV GP3 and GP5 protein based on immunoinformatics.J Cell Mol Med. 2024 Feb;28(3):e18103. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.18103. Epub 2024 Jan 12. J Cell Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 38217314 Free PMC article.
-
A candidate multi-epitope vaccine against porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus and Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae induces robust humoral and cellular response in mice.Vaccine. 2022 Apr 6;40(16):2370-2378. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2022.03.021. Epub 2022 Mar 17. Vaccine. 2022. PMID: 35307227
-
Multi-epitope vaccines: a promising strategy against viral diseases in swine.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024 Dec 20;14:1497580. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1497580. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39760092 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus vaccines: current status and strategies to a universal vaccine.Transbound Emerg Dis. 2014 Apr;61(2):109-20. doi: 10.1111/tbed.12016. Epub 2013 Jan 24. Transbound Emerg Dis. 2014. PMID: 23343057 Review.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

