Psychiatric disorders in children and adolescents with temporal lobe epilepsy: A narrative review
- PMID: 39729085
- PMCID: PMC11803279
- DOI: 10.1002/epi4.13122
Psychiatric disorders in children and adolescents with temporal lobe epilepsy: A narrative review
Abstract
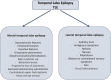
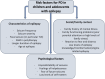
People with epilepsy (PWE) are at higher risk of psychiatric disorders (PD), disability, and reduced quality of life than the general population, especially in childhood and adolescence and when seizures originate from the temporal lobe. Temporal Lobe Epilepsy (TLE) is the most common type of focal epilepsy and can be due to structural abnormalities, or non-lesional causes, such as genetic variants. The prevalence of PD is approximately 20%-30% in people with epilepsy in general, and from 40% up to 80% in people with TLE. A higher rate of anxiety and depression disorders has been observed in association with TLE than with extra-temporal epilepsy, or idiopathic generalized epilepsy, or other chronic diseases such as diabetes. However, while the association between psychopathology and TLE has been extensively assessed in adults, only a few studies have focused on its expression in children and adolescents. In this review, we describe the prevalence, characteristics, and risk factors for PD in people with epilepsy in general and with TLE, with a specific focus on the pediatric age. In addition, we provide insights into the current knowledge of the pathophysiological bases of psychiatric symptoms in children and adolescents with TLE. PLAIN LANGUAGE SUMMARY: This review examines the frequency and characteristics of psychiatric disorders in people with temporal lobe epilepsy, with a focus on children and adolescents. Similarly to adults, younger people with epilepsy have higher rates of psychiatric disorders, such as depression and anxiety, than healthy peers or children with other chronic illnesses such as diabetes and asthma. Contributing risk factors include epilepsy duration and severity, and the effects of antiseizure medications, as well as psychological challenges, sociocultural influences, and family dynamics. Psychiatric disorders associated with temporal lobe epilepsy are relatively frequent, probably in relation to the critical role that some limbic structures in the temporal lobe, such as the amygdala and hippocampus, play in regulating emotions and behavior.
Keywords: adolescents; children; comorbidities; psychopathology; temporal lobe epilepsy.
© 2024 The Author(s). Epilepsia Open published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of International League Against Epilepsy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Pascual MR. Temporal lobe epilepsy: clinical semiology and neurophysiological studies. Semin Ultrasound CT MRI. 2007;28(6):416–423. - PubMed
-
- Gataullina S, Dulac O, Bulteau C. Temporal lobe epilepsy in infants and children. Rev Neurol (Paris). 2015;171(3):252–258. - PubMed
-
- Barba C, Rheims S, Minotti L, Grisotto L, Chabardès S, Guenot M, et al. Surgical outcome of temporal plus epilepsy is improved by multilobar resection. Epilepsia. 2022;63(4):769–776. - PubMed
-
- Blumcke I, Spreafico R, Haaker G, Coras R, Kobow K, Bien CG, et al. Histopathological findings in brain tissue obtained during epilepsy surgery. N Engl J Med. 2017;377(17):1648–1656. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical