Dilute Povidone-Iodine Irrigation: The Science of Molecular Iodine (I2) Kinetics and Its Antimicrobial Activity
- PMID: 39729104
- PMCID: PMC11661569
- DOI: 10.5435/JAAOS-D-24-00471
Dilute Povidone-Iodine Irrigation: The Science of Molecular Iodine (I2) Kinetics and Its Antimicrobial Activity
Abstract
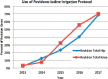
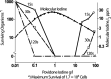
Dilute povidone-iodine (polyvinylpyrrolidone iodine [PVP-I]) irrigation in spine surgery and total joint arthroplasty has seen a rapid and substantial increase in its use during the past decade. Yet, most surgeons do not know the chemistry and biochemistry that explain its efficacy in preventing infections. PVP-I forms a complex with molecular iodine (I2), facilitating the delivery of I2 to the membrane of the infectious organism. Here, PVP-I establishes an equilibrium between complexed and noncomplexed (free) I2 in the aqueous solution. The I2 acts at numerous cellular targets of infecting organisms augmenting its role as a biocidal molecule. The paradoxical increase in the concentration of I2 that occurs with dilution of PVP-I is a result of equilibrium kinetics and is associated with an enhanced antimicrobial activity. Cytotoxicity studies have yielded conflicting results, but most endorse diluted concentrations as being less damaging to tissues. Clinical studies have verified notable reductions in surgical site infections with a 3-minute soak of 0.35% dilute povidone-iodine irrigation. Guidelines from the World Health Organization, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, and International Consensus Meeting on Musculoskeletal Infection support the use of prophylactic incisional wound irrigation with aqueous PVP-I to reduce and prevent surgical site infections.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. on behalf of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Randomised trial of intraperitoneal irrigation with low molecular weight povidone-iodine solution to reduce intra-abdominal infectious complications.J Hosp Infect. 1985 Mar;6 Suppl A:103-14. doi: 10.1016/s0195-6701(85)80054-2. J Hosp Infect. 1985. PMID: 2860153 Clinical Trial.
-
Comparison Of Intraoperative Wound Irrigation With Aqueous Povidone-Iodine Solution To Normal Saline In Preventing Surgical Site Infections.J Ayub Med Coll Abbottabad. 2023 Jul-Sep;35(3):371-374. doi: 10.55519/JAMC-03-12158. J Ayub Med Coll Abbottabad. 2023. PMID: 38404074 Clinical Trial.
-
The Toxicity and Antibacterial Effects of Povidone-Iodine Irrigation in Fracture Surgery.Orthop Surg. 2022 Sep;14(9):2286-2297. doi: 10.1111/os.13422. Epub 2022 Aug 1. Orthop Surg. 2022. PMID: 35913384 Free PMC article.
-
Diluted povidone-iodine irrigation prior to wound closure in primary and revision total joint arthroplasty of hip and knee: a review of the evidence.J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 2020 May-Jun;34(3 Suppl. 2):57-62. ADVANCES IN MUSCULOSKELETAL DISEASES AND INFECTIONS - SOTIMI 2019. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 2020. PMID: 32856441
-
Povidone-iodine: use in hand disinfection, skin preparation and antiseptic irrigation.Int Wound J. 2008 Jun;5(3):376-87. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-481X.2007.00405.x. Int Wound J. 2008. PMID: 18593388 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Wound healing by enhancing cell proliferation: a thermoreversible formulation containing raloxifene.Cell Tissue Bank. 2025 Apr 24;26(2):22. doi: 10.1007/s10561-025-10171-6. Cell Tissue Bank. 2025. PMID: 40272605
References
-
- Hart A, Hernandez NM, Abdel MP, Mabry TM, Hanssen AD, Perry KI: Povidone-iodine wound lavage to prevent infection after revision total hip and knee arthroplasty: An analysis of 2,884 cases. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2019;101:1151-1159. - PubMed
-
- Kessler J, Obinger C, Eales G: Factors influencing the study of peroxidase-generated iodine species and implications for thyroglobulin synthesis. Thyroid 2008;18:769-774. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

