Differences in Blood and Cerebrospinal Fluid Between Parkinson's Disease and Related Diseases
- PMID: 39729132
- PMCID: PMC11680620
- DOI: 10.1007/s10571-024-01523-z
Differences in Blood and Cerebrospinal Fluid Between Parkinson's Disease and Related Diseases
Abstract
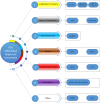
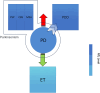
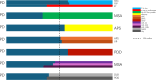
It is difficult to distinguish Parkinson's disease (PD) in the early stage from those of various disorders including atypical Parkinson's syndrome (APS), vascular parkinsonism (VP), and even essential tremor (ET), because of the overlap of symptoms. Other, more challenging problems will arise when Parkinson's disease develops into Parkinson's disease dementia (PDD) in the middle and late stages. At this time, the differential diagnosis of PDD and DLB becomes thorny. These complicate the diagnostic process for PD, which traditionally heavily relies on symptomatic assessment and treatment response. Recent advances have identified several biomarkers in the blood and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), including α-synuclein, lysosomal enzymes, fatty acid-binding proteins, and neurofilament light chain, whose concentration differs in PD and the related diseases. However, not all these molecules can effectively discriminate PD from related disorders. This review advocates for a paradigm shift toward biomarker-based diagnosis to effectively distinguish between PD and similar conditions. These biomarkers may reflect the diversity that exist among different diseases and provide an effective way to accurately understand their mechanisms. This review focused on blood and CSF biomarkers of PD that may have differential diagnostic value and the related molecular measurement methods with high diagnostic performance due to emerging technologies.
Keywords: Atypical Parkinsonian disorders; Biomarkers; Dementia and movement disorders; Differential diagnosis; Parkinson’s disease.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: Author LH was employed by ICON Plc. The remaining authors have no relevant financial or nonfinancial interests to disclose. Ethical Approval: Not applicable. Consent to Participate: Not applicable. Consent to Publish: All authors have read and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Cerebrospinal fluid and blood neurofilament light chain in Parkinson's disease and atypical parkinsonian syndromes: a systematic review and Bayesian network meta-analysis.J Neurol. 2025 Apr 3;272(4):311. doi: 10.1007/s00415-025-13051-x. J Neurol. 2025. PMID: 40180649
-
CSF and blood biomarkers for Parkinson's disease.Lancet Neurol. 2019 Jun;18(6):573-586. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(19)30024-9. Epub 2019 Apr 10. Lancet Neurol. 2019. PMID: 30981640 Review.
-
Accuracy of a panel of 5 cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers in the differential diagnosis of patients with dementia and/or parkinsonian disorders.Arch Neurol. 2012 Nov;69(11):1445-52. doi: 10.1001/archneurol.2012.1654. Arch Neurol. 2012. PMID: 22925882
-
Parkinson's Disease Diagnostic Observations (PADDO): study rationale and design of a prospective cohort study for early differentiation of parkinsonism.BMC Neurol. 2018 May 16;18(1):69. doi: 10.1186/s12883-018-1072-x. BMC Neurol. 2018. PMID: 29764386 Free PMC article.
-
Differential role of CSF fatty acid binding protein 3, α-synuclein, and Alzheimer's disease core biomarkers in Lewy body disorders and Alzheimer's dementia.Alzheimers Res Ther. 2017 Jul 28;9(1):52. doi: 10.1186/s13195-017-0276-4. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2017. PMID: 28750675 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Neuronally Derived Extracellular Vesicles' Oligomeric and p129-α-Synuclein Levels for Differentiation of Parkinson's Disease from Essential Tremor.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Apr 17;26(8):3819. doi: 10.3390/ijms26083819. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40332541 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aerts MB, Esselink RA, Abdo WF, Bloem BR, Verbeek MM (2012) CSF α-synuclein does not differentiate between Parkinsonian disorders. Neurobiol Aging 33:430.e1-430.e3. 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2010.12.001 - PubMed
-
- Amin J, Erskine D, Donaghy PC, Surendranathan A, Swann P, Kunicki AP, Boche D, Holmes C, McKeith IG, O’Brien JT, Teeling JL, Thomas AJ (2022) Inflammation in dementia with Lewy bodies. Neurobiol Dis 168:105698. 10.1016/j.nbd.2022.105698 - PubMed
-
- Anastassiadis C, Martinez-Valbuena I, Vasilevskaya A, Thapa S, Hadian M, Morales-Rivero A, Mora-Fisher D, Salvo C, Taghdiri F, Sato C, Moreno D, Anor CJ, Misquitta K, Couto B, Tang-Wai DF, Lang AE, Fox SH, Rogaeva E, Kovacs GG, Tartaglia MC (2024) CSF α-synuclein seed amplification assay in patients with atypical Parkinsonian disorders. Neurology 103(6):e209818. 10.1016/j.nbd.2022.10569810.1212/WNL.0000000000209818 - PubMed
-
- Armstrong MJ, Okun MS (2020) Diagnosis and treatment of Parkinson disease: a review. JAMA 323:548–560. 10.1001/jama.2019.22360 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

