Unveiling chemotherapy-induced immune landscape remodeling and metabolic reprogramming in lung adenocarcinoma by scRNA-sequencing
- PMID: 39729352
- PMCID: PMC11677239
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.95988
Unveiling chemotherapy-induced immune landscape remodeling and metabolic reprogramming in lung adenocarcinoma by scRNA-sequencing
Abstract
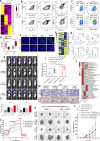
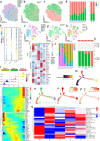
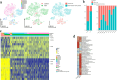
Chemotherapy is widely used to treat lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD) patients comprehensively. Considering the limitations of chemotherapy due to drug resistance and other issues, it is crucial to explore the impact of chemotherapy and immunotherapy on these aspects. In this study, tumor samples from nine LUAD patients, of which four only received surgery and five received neoadjuvant chemotherapy, were subjected to scRNA-seq analysis. In vitro and in vivo assays, including flow cytometry, immunofluorescence, Seahorse assay, and tumor xenograft models, were carried out to validate our findings. A total of 83,622 cells were enrolled for subsequent analyses. The composition of cell types exhibited high heterogeneity across different groups. Functional enrichment analysis revealed that chemotherapy drove significant metabolic reprogramming in tumor cells and macrophages. We identified two subtypes of macrophages: Anti-mac cells (CD45+CD11b+CD86+) and Pro-mac cells (CD45+CD11b+ARG +) and sorted them by flow cytometry. The proportion of Pro-mac cells in LUAD tissues increased significantly after neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Pro-mac cells promote tumor growth and angiogenesis and also suppress tumor immunity. Moreover, by analyzing the remodeling of T and B cells induced by neoadjuvant therapy, we noted that chemotherapy ignited a relatively more robust immune cytotoxic response toward tumor cells. Our study demonstrates that chemotherapy induces metabolic reprogramming within the tumor microenvironment of LUAD, particularly affecting the function and composition of immune cells such as macrophages and T cells. We believe our findings will offer insight into the mechanisms of drug resistance and provide novel therapeutic targets for LUAD in the future.
Keywords: lung adenocarcinoma; cancer biology; human; metabolic reprogramming; neoadjuvant chemotherapy; phenotype atlas.
© 2024, Huang, Wu, Bi et al.
Conflict of interest statement
YH, GW, GB, LC, JL, ML, HZ, GS, ZH, ZC, ZL, WJ, QW, JX, SY, CZ No competing interests declared
Figures

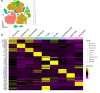
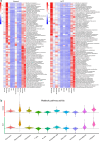
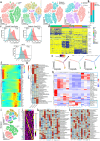


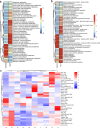



Update of
- doi: 10.1101/2024.02.18.580893
- doi: 10.7554/eLife.95988.1
- doi: 10.7554/eLife.95988.2
References
-
- Anand P, Guillaumet-Adkins A, Dimitrova V, Yun H, Drier Y, Sotudeh N, Rogers A, Ouseph MM, Nair M, Potdar S, Isenhart R, Kloeber JA, Vijaykumar T, Niu L, Vincent T, Guo G, Frede J, Harris MH, Place AE, Silverman LB, Teachey DT, Lane AA, DeAngelo DJ, Aster JC, Bernstein BE, Lohr JG, Knoechel B. Single-cell RNA-seq reveals developmental plasticity with coexisting oncogenic states and immune evasion programs in ETP-ALL. Blood. 2021;137:2463–2480. doi: 10.1182/blood.2019004547. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Aran D, Looney AP, Liu L, Wu E, Fong V, Hsu A, Chak S, Naikawadi RP, Wolters PJ, Abate AR, Butte AJ, Bhattacharya M. Reference-based analysis of lung single-cell sequencing reveals a transitional profibrotic macrophage. Nature Immunology. 2019;20:163–172. doi: 10.1038/s41590-018-0276-y. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bernhagen J, Krohn R, Lue H, Gregory JL, Zernecke A, Koenen RR, Dewor M, Georgiev I, Schober A, Leng L, Kooistra T, Fingerle-Rowson G, Ghezzi P, Kleemann R, McColl SR, Bucala R, Hickey MJ, Weber C. MIF is a noncognate ligand of CXC chemokine receptors in inflammatory and atherogenic cell recruitment. Nature Medicine. 2007;13:587–596. doi: 10.1038/nm1567. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bondarenko M, Le Grand M, Shaked Y, Raviv Z, Chapuisat G, Carrère C, Montero MP, Rossi M, Pasquier E, Carré M, André N. Metronomic chemotherapy modulates clonal interactions to prevent drug resistance in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancers. 2021;13:2239. doi: 10.3390/cancers13092239. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

