Role of Toll-like receptor 2 during infection of Leptospira spp: A systematic review
- PMID: 39729468
- PMCID: PMC11676585
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0312466
Role of Toll-like receptor 2 during infection of Leptospira spp: A systematic review
Abstract
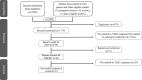
The involvement of Toll-like receptor 2 (TLR2) in leptospirosis is poorly understood. Our systematic review examined its role across in-vitro, in-vivo, ex-vivo, and human studies. Original articles published in English up to January 2024, exploring the role of TLR2 during leptospirosis, were selected from databases including PubMed, Web of Science, Scopus, Trip, and Google Scholar. Cochrane guidelines and Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses were followed by this systematic review. The National Institute of Health Quality Assessment tool, Systematic Review Centre for Laboratory Animal Experimentation risk of bias tool, and Office of Health Assessment and Translation extended tool were used to assess the risk of bias of the studies. Out of 2458 studies retrieved, 35 were selected for the systematic review. These comprised 3 human, 17 in-vitro, 5 in-vivo, 3 ex-vivo, and 7 studies with combined experimental models. We assessed the direct TLR2 expression and indirect TLR2 involvement via the secretion/mRNA expression of immune effectors during leptospirosis. Notably, we observed the secretion/mRNA expression of several cytokines (IL6, IL8, IL-1β, TNFα, IFNγ, IL10, CCL2/MCP-1, CCL10, COX2, CXCL1/KC, CXCL2/MIP2) and immune effectors (hBD2, iNOS, Fibronectin, Oxygen, and Nitrogen reactive species) as key aspects of host TLR2 responses during leptospirosis. Even though increased TLR2 expression in in-vivo and in-vitro studies was evident, human studies reported mixed results showing that the postulated effect of TLR2 response based on other studies may not be valid for human leptospirosis. Besides the role of TLR2 in response to leptospirosis, the involvement of TLR4 and TLR5 was identified in in-vitro and in-vivo studies. TLR2 expression is inconclusive during human leptospirosis and further studies are needed to examine the immune effector regulation, through TLR2 for mitigating the harmful effects and promoting effective immune responses.
Copyright: © 2024 Kappagoda et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Stimson AM. Note on an Organism Found in Yellow-Fever Tissue. Public Heal Reports. 1907;22(18):541.
-
- Bharti AR, Nally JE, Ricaldi JN, Matthias MA, Diaz MM, Lovett MA, et al. Reviews Leptospirosis: a zoonotic disease of global importance. 2003;3(December):757–71. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous