Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on lung cancer diagnosis in northern Poland-addressing the COVID-19 debt
- PMID: 39729487
- PMCID: PMC11676660
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0316261
Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on lung cancer diagnosis in northern Poland-addressing the COVID-19 debt
Abstract
Introduction: Lung cancer, one of the leading causes of death due to neoplasms, requires prompt diagnosis and immediate treatment. The COVID-19 pandemic affected healthcare systems worldwide, having adverse effects on all aspects, particularly on the fate of patients with suspected neoplastic diseases. Limited access to healthcare, disruptions in regular operations (reassigning roles to some wards), postponed hospital admissions, prolonged diagnostic processes, and other factors have collectively led to the phenomenon known as COVID-19 debt.
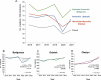
Material and methods: A retrospective analysis covered statistical data concerning the diagnosis of lung cancer obtained from three centres in northern Poland (Olsztyn, Bydgoszcz, Gdansk) and concerning years 2016 to 2022. Relative risks (RR) with 95% confidence intervals (CI) for cancer event were calculated. Before the pandemic, these centers prioritized the diagnosis of suspected lung cancer cases, which was subsequently disrupted during the pandemic due to various factors.
Results: The COVID-19 pandemic led to a decrease in diagnosed lung cancer cases, especially in hospitals repurposed for COVID-19 care. A statistically significant trend in lung cancer incidence per 100,000 inhabitants was observed specifically in healthcare centers that maintained normal operations without disruption.
Conclusion: The concept of the COVID debt helps explain changes in lung cancer diagnosis during and post-pandemic, highlighting the need for increased public awareness and intensified diagnostic efforts to facilitate earlier disease detection.
Copyright: © 2024 Romaszko-Wojtowicz et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Lung cancer. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/lung-cancer. Accessed 13 Jan 2024.
-
- IARC–INTERNATIONAL AGENCY FOR RESEARCH ON CANCER. https://www.iarc.who.int/. Accessed 13 Jan 2024.
-
- Reyes R, López-Castro R, Auclin E, et al. (2021) MA03.08 Impact of COVID-19 Pandemic in the Diagnosis and Prognosis of Lung Cancer. Journal of Thoracic Oncology 16:S141.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical