BCMA-directed CAR T-cell therapy in patients with multiple myeloma and CNS involvement
- PMID: 39729503
- PMCID: PMC11925525
- DOI: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2024014345
BCMA-directed CAR T-cell therapy in patients with multiple myeloma and CNS involvement
Abstract
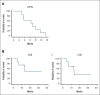
We investigated B-cell maturation antigen-directed chimeric antigen receptor T-cell (CAR-T) therapy in patients with relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma (MM) and central nervous system (CNS) involvement. Ten patients received either idecabtagene vicleucel (n = 6) or ciltacabtagene autoleucel (n = 4), where brain/cranial nerve and/or spinal cord involvement/leptomeningeal disease were evident on either magnetic resonance imaging (100%) and/or cerebrospinal fluid (40%). Eight patients had their CNS diagnosis before CAR-T therapy, and two were diagnosed within 14 days post-infusion. Seven received CNS-directed therapy during bridging before CAR-T therapy. There were no excess toxicities: no cytokine release syndrome grade ≥3; 10% immune effector cell-associated neurotoxicity syndrome (ICANS) grade 3; and no ICANS grade 4. Two patients experienced delayed but treatable neurotoxicity, with no reported parkinsonian side effects. The best overall response rate was 80% (≥70% very good partial response) and a 100% CNS response. With a median follow-up of 381 days, patients with CNS myeloma diagnosed before CAR-T therapy (n = 8) had a median overall survival and progression-free survival (PFS) of 13.3 and 6.3 months, respectively. Best outcomes were observed in 4 patients who had a response to bridging therapy, suggesting that optimizing pre-CAR-T therapy may be key for improved outcomes. Our study suggests that CAR-T therapy in patients with CNS MM is safe and feasible, and screening for CNS involvement before CAR-T therapy could be warranted in high-risk patients. The excellent initial response but relatively short PFS suggests consideration for post-CAR-T maintenance. Larger studies are needed to confirm these findings.
© 2025 American Society of Hematology. Published by Elsevier Inc. Licensed under Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0), permitting only noncommercial, nonderivative use with attribution. All other rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: M.R.G. reports consulting or advisory role fees from Bristol Myers Squibb, Boxer Capital LLC, and Arcellx. O.C.P. reports consulting or advisory role fees from Bristol Myers Squibb/Celgene/Juno and Legend Biotech. A. Cohen reports consulting or advisory role fees from AbbVie, Arcellx, Bristol Myers Squibb, GlaxoSmithKline, Ichnos Sciences, ITeos Therapeutics, Janssen Oncology, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche/Genentech, and Takeda; research funding from Genentech/Roche (institutional), GlaxoSmithKline (institutional), Janssen Oncology (institutional), and Novartis (institutional); patents, royalties, other intellectual property with patents related to CAR T cells and biomarkers of cytokine release syndrome; and travel, accommodations, and expenses paid by AbbVie, Bristol Myers Squibb, Ichnos Sciences, and Janssen Oncology. D.V. reports consulting or advisory role fees from Celgene, CSL Behring, Genentech, GlaxoSmithKline, Janssen, Karyopharm Therapeutics, Oncopeptides, Sanofi, and Takeda; research funding from Active Biotech (institutional) and Takeda (institutional); and travel, accommodations, and expenses paid by Karyopharm Therapeutics and Takeda. A. Chung reports consulting or advisory role fees from Janssen; and research funding from AbbVie (institutional), Bristol Myers Squibb/Celgene (institutional), Caelum Biosciences (institutional), Cellectis (institutional), Janssen (institutional), k36 Therapeutics (institutional), and Merck (institutional). C.J.F. reports stock and other ownership interests in Affimed (AFMD). P.V. reports consulting or advisory role fees from AbbVie/Genentech, Bristol Myers Squibb (Mexico), GlaxoSmithKline, Janssen, Karyopharm Therapeutics, Pfizer, and Sanofi; research funding from AbbVie (institutional), GlaxoSmithKline (institutional), Janssen (institutional), and Teneobio (institutional); travel, accommodations, and expenses from Sanofi; and uncompensated relationships with GlaxoSmithKline. D.K.H. reports consulting or advisory role fees from Bristol Myers Squibb; and research funding from Bristol Myers Squibb/Celgene. K.K.P. reports consulting or advisory role fees from AbbVie, Arcellx, Bristol Myers Squibb, Caribou Biosciences, Celgene, Cellectis, Janssen, Karyopharm Therapeutics, Merck, Pfizer, and Takeda; research funding from AbbVie/Genentech, Allogene Therapeutics, Celgene/Bristol Myers Squibb, Cellectis, Janssen, Nektar, Precision Biosciences, and Takeda; and travel, accommodations, and expenses from Bristol Myers Squibb.
Figures
References
-
- Schuster SJ, Bishop MR, Tam CS, et al. Tisagenlecleucel in adult relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. N Engl J Med. 2019;380(1):45–56. - PubMed
-
- Munshi NC, Anderson LD, Jr., Shah N, et al. Idecabtagene vicleucel in relapsed and refractory multiple myeloma. N Engl J Med. 2021;384(8):705–716. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

