Improving patient satisfaction based on service quality in clinical trials: A cross-sectional study
- PMID: 39729511
- PMCID: PMC11676555
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0313340
Improving patient satisfaction based on service quality in clinical trials: A cross-sectional study
Abstract
Background: Participants' satisfaction is an important factor in securing competitiveness in clinical trials. In many industries, such as healthcare, customer service quality has been analyzed to increase customer satisfaction. However, no study so far has attempted to measure participants' perceptions of service quality in the clinical trial area and identify its effect on participant satisfaction.
Objective: This study examined the experiences and perceptions of clinical trial participants in terms of service quality and identified the factors that impact participant satisfaction in clinical trials.
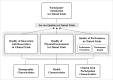
Methods: This study used a cross-sectional descriptive and explanatory research design. Data were collected from March 29 to May 26, 2023, via a survey. The survey was conducted with 206 adults participating in clinical trials at two hospitals in Korea. The collected data were analyzed using descriptive statistics, independent t-tests, one-way ANOVA, Pearson's correlation, and multiple linear regression analysis.
Results: Participants' perceptions of the service quality and their satisfaction in clinical trials were generally positive. The variables that significantly predicted participant satisfaction in clinical trials included quality of interaction with researchers, physical environment, performance results in clinical trials, changes in health status after participating in the trial, and consideration of discontinuing the trial.
Conclusions: Participants' perception of the service quality significantly affected their satisfaction in clinical trials. Thus, all components of service quality should be considered in the overall clinical trial process to increase participants' satisfaction.
Copyright: © 2024 Lee et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
References
-
- National Institutes of Health [NIH]. Trends, charts, and maps. 2024. [cited 14 February 2024]. In: Clinicaltrials.gov [Internet]. Available from: https://classic.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/resources/trends
-
- Tantoy IY, Bright AN, Paelmo E, Moreland EI, Trost AN, Pasquesi J, et al.. Patient satisfaction while enrolled in clinical trials: A literature review. Patient Exp J. 2021;8: 125–135. doi: 10.35680/2372-0247.1509 - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical