Smear layer removal comparing conventional irrigation, passive ultrasonic irrigation, EndoActivator System, and a new sonic device (Perfect Clean System) by scanning electron microscopy: An ex vivo study
- PMID: 39729517
- PMCID: PMC11676573
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0314940
Smear layer removal comparing conventional irrigation, passive ultrasonic irrigation, EndoActivator System, and a new sonic device (Perfect Clean System) by scanning electron microscopy: An ex vivo study
Abstract
Aim: This study evaluated the smear layer removal provided by conventional, sonic, and ultrasonic irrigation techniques.
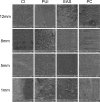
Methodology: Forty extracted human mandibular first premolars were selected and instrumented using the ProTaper Next System files and 2.5% sodium hypochlorite. Afterward, they were divided into 4 groups (n. 10) according to the irrigation technique used to perform the final irrigation with a chelating solution (17% EDTA): conventional irrigation (CI), passive ultrasonic irrigation (PUI), EndoActivator System (EAS), and Perfect Clean System (PCS). The smear layer removal was determined through a score after evaluating scanning electron microscope images (1.000x) obtained at 1, 5, 8, and 12mm from the working length (WL). Statistical analyses were carried out by the Kruskal-Wallis and Dunn's tests with a significance level of 5% (P < 0.05).
Results: All irrigation techniques were unable to promote an effective smear layer removal at 1mm from the WL in comparison with the other locations (P < .05). At 5, 8, and 12mm from the WL, no statistically significant differences were observed among CI, PUI, EAS, and PCS (P > 0.05). At 12mm from the WL, statistically significant differences were only identified after comparing PCS and CI (P < .05).
Conclusion: The smear layer removal was only efficient at 5, 8, and 12 from the WL with no significant statistical differences among CI, PUI, EAS, and PCS (P > 0.05).
Copyright: © 2024 Gonçalves et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Smear layer removal and canal cleanliness using different irrigation systems (EndoActivator, EndoVac, and passive ultrasonic irrigation): field emission scanning electron microscopic evaluation in an in vitro study.J Endod. 2013 Nov;39(11):1456-60. doi: 10.1016/j.joen.2013.07.028. Epub 2013 Sep 6. J Endod. 2013. PMID: 24139274
-
Canal cleanliness using different irrigation activation systems: a SEM evaluation.Clin Oral Investig. 2017 Dec;21(9):2681-2687. doi: 10.1007/s00784-017-2070-x. Epub 2017 Feb 9. Clin Oral Investig. 2017. PMID: 28185091
-
Assessment of Smear Layer Removal and Penetration Depth of Root Canal Irrigant Using Different Irrigation Activation Systems: A Comparative Study.J Contemp Dent Pract. 2024 Apr 1;25(4):331-334. doi: 10.5005/jp-journals-10024-3626. J Contemp Dent Pract. 2024. PMID: 38956847
-
Efficacy of irrigant activation techniques in removing intracanal smear layer and debris from mature permanent teeth: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Int Endod J. 2018 Jun;51(6):605-621. doi: 10.1111/iej.12877. Epub 2017 Dec 22. Int Endod J. 2018. PMID: 29178166
-
Efficacy of sonic and ultrasonic activation during endodontic treatment: a Meta-analysis of in vitro studies.Acta Odontol Scand. 2022 Nov;80(8):588-595. doi: 10.1080/00016357.2022.2061591. Epub 2022 Apr 17. Acta Odontol Scand. 2022. PMID: 35430959
Cited by
-
Multisonic Ultracleaning and Laser-Activated Irrigation Effect Compared to Passive Ultrasonic Activation for Debridement in Minimally Invasive Instrumentation of Necrotic Oval Root Canals: An Ex Vivo Histological Analysis.J Clin Med. 2025 Apr 10;14(8):2597. doi: 10.3390/jcm14082597. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 40283427 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lui K, Liu H, Wang H, Yang X, Huang D, Zhou X, et al.. An application framework of 3D assessment image registration accuracy and untouched surface area in canal instrumentation laboratory research with micro-computed tomography. Clin Oral Investig. 2023;27(2):715–25. doi: 10.1007/s00784-022-04819-w - DOI - PubMed
-
- Morago A, Ordinola-Zapata R, Ferrer-Luque CM, Baca P, Ruiz-Linares M, Arias-Moliz MT. Influence of Smear Layer on the Antimicrobial Activity of a Sodium Hypochlorite/Etidronic Acid Irrigating Solution in Infected Dentin. J Endod. 2016;42(11):1647–50. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources