Assessing the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on uptake and experiences of gestational diabetes mellitus screening in Ontario: A parallel convergent mixed-methods study
- PMID: 39729523
- PMCID: PMC11676491
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0315983
Assessing the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on uptake and experiences of gestational diabetes mellitus screening in Ontario: A parallel convergent mixed-methods study
Abstract
Objective: Gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) is a common medical complication of pregnancy that leads to adverse outcomes for both infants and pregnant people. Early detection and treatment can mitigate these negative outcomes. The COVID-19 pandemic strained healthcare and laboratory services, including GDM screening programs. Adapted GDM screening guidelines were introduced in many jurisdictions. This study examined changes in uptake, modality, and experiences of GDM screening in Ontario, Canada during the COVID-19 pandemic.
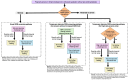
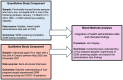
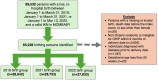
Methods: This convergent mixed-method study involved a population-based retrospective cohort analysis of Ontario-based health administrative data to describe and compare gestational diabetes screening rates among 85,228 individuals with live, in-hospital births between January 1-March 31 before (2019) and during the COVID-19 pandemic (2021 and 2022). Descriptive analyses were conducted for GDM screening pathways aligning with usual and pandemic-adapted screening guidance. Qualitative descriptive interviews were conducted about experiences and decision-making of GDM screening with 43 Ontario residents who gave birth between May 2020 and December 2021. Data were integrated during the design and interpretation phases.
Results: There were small but significant increases in GDM screening during the pandemic; likelihood of screening completion using any modality increased in 2021 and 2022 compared to 2019. Testing modality shifted; the alternate screening strategies introduced during COVID-19 were adopted by clinicians. Interview participants perceived GDM screening to be important and obligatory but accompanied by a degree of stress about potential COVID-19 exposure.
Conclusion: Despite health system challenges experienced in Ontario during the COVID-19 pandemic, GDM screening rates increased in the study population, demonstrating the success of adapted GDM screening guidelines. Decisions about screening modalities were driven by clinician expertise, and interview participants were satisfied to provide informed consent to these recommendations.
Copyright: © 2024 Hadid et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Gestational diabetes screening from the perspective of consumers: Insights from early in the COVID-19 pandemic and opportunities to optimise experiences.Aust N Z J Obstet Gynaecol. 2023 Apr;63(2):154-162. doi: 10.1111/ajo.13600. Epub 2022 Aug 12. Aust N Z J Obstet Gynaecol. 2023. PMID: 35962529
-
Impact of a modified screening approach during the COVID-19 pandemic on the diagnosis and outcomes of gestational diabetes mellitus: A population-level analysis of 90,518 pregnant women.Diabet Med. 2024 Feb;41(2):e15247. doi: 10.1111/dme.15247. Epub 2023 Oct 30. Diabet Med. 2024. PMID: 37857500
-
Clinicians' perspectives on gestational diabetes screening during the global COVID-19 pandemic in Australia.Aust N Z J Obstet Gynaecol. 2023 Apr;63(2):163-170. doi: 10.1111/ajo.13601. Epub 2022 Aug 12. Aust N Z J Obstet Gynaecol. 2023. PMID: 35962532 Free PMC article.
-
Comparing the screening methods for gestational diabetes mellitus before and during the COVID-19 pandemic: A systematic review.J Diabetes Investig. 2024 Apr;15(4):500-516. doi: 10.1111/jdi.14128. Epub 2023 Dec 16. J Diabetes Investig. 2024. PMID: 38102930 Free PMC article.
-
Screening for Gestational Diabetes during the COVID-19 Pandemic-Current Recommendations and Their Consequences.Medicina (Kaunas). 2021 Apr 15;57(4):381. doi: 10.3390/medicina57040381. Medicina (Kaunas). 2021. PMID: 33920937 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

