Fourier analysis of signal dependent noise images
- PMID: 39730404
- PMCID: PMC11681241
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-78299-1
Fourier analysis of signal dependent noise images
Abstract
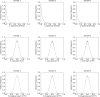
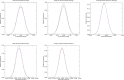
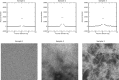
An archetype signal dependent noise (SDN) model is a component used in analyzing images or signals acquired from different technologies. This model-component may share properties with stationary normal white noise (WN). Measurements from WN images were used as standards for making comparisons with SDN in both the image domain (ID) and Fourier domain (FD). The ID wavelet expansion was applied to WN images (n = 1000). Orthogonality conditions were used to parametrically model the variance decomposition, as described in both domains. FD components were investigated with probability density function modeling and summarized measures. SDN images were constructed by multiplying both simulated and clinical mammograms (both with n = 1000) by WN. The variance decomposition for both WN and SDN decreases exponentially as a parametric function of the ID expansion level; expansion image variances for both types of noise were captured similarly in the Fourier plane corresponding with the ID parametric model. The Fourier transform of WN has a uniform power spectrum distributed exponentially; SDN has similar attributes. Fourier inversion of the lag-autocorrelation performed in the FD produced a statistical estimation of the SDN's image factor. These findings are counterintuitive as SDN can be nonstationary in the ID but have stationary attributes in the FD.
Keywords: Fourier analysis; Mammographic simulations; Mammography; Signal dependent noise; Wavelet expansion.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Ethics and consent to participate: All methods were carried out in accordance with relevant guidelines and regulations. All experimental procedures were approved by the Institutional Review Board (IRB) of the University of South Florida, Tampa, FL under protocol #Ame13_104715. Mammography data was collected retrospectively on a waiver for informed consent approved by the IRB of the University of South Florida, Tampa, FL under protocol #Ame13_104715. Consent of publication: The work does not contain personal identifiers.
Figures


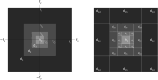
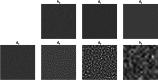
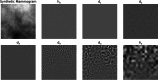
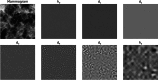






References
-
- Foi, A., Katkovnik, V., & Egiazarian, E. Signal-dependent noise removal in pointwise shape-adaptive DCT domain with locally adaptive variance. In 2007 15th European Signal Processing Conference, IEEE, pp. 2159–2163 (2007).
-
- Torricelli, G., Argenti, F., & Alparone, L. Modelling and assessment of signal-dependent noise for image de-noising. In 2002 11th European signal processing conference, IEEE, pp. 1–4 (2002).
-
- Hirakawa, K. Fourier and filterbank analyses of signal-dependent noise. In 2008 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, IEEE, pp. 3517–3520 (2008).
-
- Thai, T. H., Retraint, F. & Cogranne, R. Generalized signal-dependent noise model and parameter estimation for natural images. Signal Process.114, 164–170 (2015). - DOI
-
- Oh, B. T., Kuo, C.-C. J., Sun, S., & Lei, S. Film grain noise modeling in advanced video coding. In Visual Communications and Image Processing 2007, vol. 6508: SPIE, pp. 362–373 (2007).
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

