Analysis of complete genomes of Mycobacterium tuberculosis sublineage 2.1 (Proto-Beijing) revealed the presence of three pe_pgrs3-pe_pgrs4-like genes
- PMID: 39730410
- PMCID: PMC11680800
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-79351-w
Analysis of complete genomes of Mycobacterium tuberculosis sublineage 2.1 (Proto-Beijing) revealed the presence of three pe_pgrs3-pe_pgrs4-like genes
Abstract
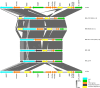
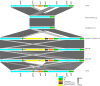
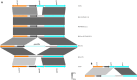
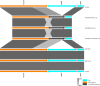
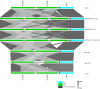
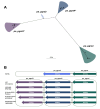
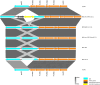
Mycobacterium tuberculosis Complex (MTBC), the etiological agent of tuberculosis (TB), demonstrates considerable genotypic diversity with distinct geographic distributions and variable virulence profiles. The pe-ppe gene family is especially noteworthy for its extensive variability and roles in host immune response modulation and virulence enhancement. We sequenced an Mtb genotype L2.1 isolate from Chiangrai, Northern Thailand, using second and third-generation sequencing technologies. Comparative genomic analysis with two additional L2.1 isolates and two L2.2.AA3 (Asia Ancestral 3 Beijing) isolates revealed significant pe-ppe gene variations. Notably, all L2.1 isolates harbored three copies of pe_pgrs3-pe_pgrs4-like genes (pe_pgrs3*, pe_pgrs4*, and pe_pgrs4), different from L2.2.AA3 and H37Rv strains. Additionally, ppe53 was duplicated in all but H37Rv, and ppe50 was deleted in L2.1 isolates, contrasting with an extended ppe50 in an L2.2 isolate (Mtb 18b), which contains an additional SVP motif. Complete deletion of ppe66 and loss of wag22 were observed in L2.1 isolates. These findings highlight the high structural variability of the pe-ppe gene family, emphasizing its complex roles in Mtb-host immune interactions. This genetic complexity offers potentially critical insights into mycobacterial pathogenesis, with significant implications for vaccine development and diagnostics.
Keywords: Mycobacterium tuberculosis; Pe-ppe; pe_pgrs3; pe_pgrs4; Lineage 2.1; Proto-Beijing genotype.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
PE_PGRS3 of Mycobacterium tuberculosis is specifically expressed at low phosphate concentration, and its arginine-rich C-terminal domain mediates adhesion and persistence in host tissues when expressed in Mycobacterium smegmatis.Cell Microbiol. 2018 Dec;20(12):e12952. doi: 10.1111/cmi.12952. Epub 2018 Sep 26. Cell Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 30192424
-
Global genetic diversity of Mycobacterium tuberculosis L2.1 based on pe-ppe gene family.Infect Genet Evol. 2025 Jul 22;134:105802. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2025.105802. Online ahead of print. Infect Genet Evol. 2025. PMID: 40706824
-
Recombination in pe/ppe genes contributes to genetic variation in Mycobacterium tuberculosis lineages.BMC Genomics. 2016 Feb 29;17:151. doi: 10.1186/s12864-016-2467-y. BMC Genomics. 2016. PMID: 26923687 Free PMC article.
-
Phylogeny to function: PE/PPE protein evolution and impact on Mycobacterium tuberculosis pathogenicity.Mol Microbiol. 2015 Jun;96(5):901-16. doi: 10.1111/mmi.12981. Epub 2015 Mar 30. Mol Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 25727695 Review.
-
PE and PPE Genes: A Tale of Conservation and Diversity.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;1019:191-207. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-64371-7_10. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017. PMID: 29116636 Review.
References
-
- Gagneux, S. Ecology and evolution of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Nat. Rev. Microbiol.16, 202–213 (2018). - PubMed
-
- Rutaihwa, L. K. et al. Multiple introductions of Mycobacterium tuberculosis Lineage 2–Beijing Into Africa over centuries. Front. Ecol. Evol.7, 112 (2019).
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

