Exploratory Analysis of Radiomics and Pathomics in Uterine Corpus Endometrial Carcinoma
- PMID: 39730425
- PMCID: PMC11680997
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-78987-y
Exploratory Analysis of Radiomics and Pathomics in Uterine Corpus Endometrial Carcinoma
Abstract
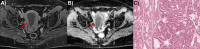
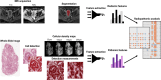
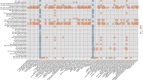
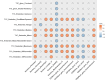
Uterine corpus endometrial carcinoma (EC) is one of the most common malignancies in the female reproductive system, characterized by tumor heterogeneity at both radiological and pathological scales. Both radiomics and pathomics have the potential to assess this heterogeneity and support EC diagnosis. This study examines the correlation between radiomics features from Apparent Diffusion Coefficient (ADC) maps and post-contrast T1 (T1C) images with pathomic features from pathology images in 32 patients from the CPTAC-UCEC database. 91 radiomics features were extracted from ADC maps and T1C images, and 566 pathomic features from cell detections and cell density maps at four different resolutions. Spearman's correlation and Bayes Factor analysis were used to evaluate radio-pathomic correlations. Significant cross-scale correlations were found, with strengths ranging from 0.57 to 0.89 in absolute value (9.47 × 104 < BF < 4.77 × 1014) for the ADC task, and from 0.64 and 0.70 (1.80 × 104 < BF < 5.69 × 105) for the T1C task. Most significant and high cross-scale associations were observed between ADC textural features and features from cell density maps. Correlations involving morphometric features and ADC and T1C first-order features were also observed, reflecting variations in tumor aggressiveness and tissue composition. These findings suggest that correlating radiomic features from ADC and T1C features with histopathological features can enhance understanding of EC intratumoral heterogeneity.
Keywords: Digital pathology; Endometrial carcinoma; MRI; Pathomics; Radiomics; Uterine corpus.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The relationship between radiomics and pathomics in Glioblastoma patients: Preliminary results from a cross-scale association study.Front Oncol. 2022 Oct 6;12:1005805. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.1005805. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36276163 Free PMC article.
-
Magnetic resonance imaging-based radiomics analysis of the differential diagnosis of ovarian clear cell carcinoma and endometrioid carcinoma: a retrospective study.Jpn J Radiol. 2024 Jul;42(7):731-743. doi: 10.1007/s11604-024-01545-z. Epub 2024 Mar 12. Jpn J Radiol. 2024. PMID: 38472624 Free PMC article.
-
MRI-based radiomics and ADC values are related to recurrence of endometrial carcinoma: a preliminary analysis.BMC Cancer. 2021 Nov 24;21(1):1266. doi: 10.1186/s12885-021-08988-x. BMC Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34819042 Free PMC article.
-
Radiomics analysis of apparent diffusion coefficient in cervical cancer: A preliminary study on histological grade evaluation.J Magn Reson Imaging. 2019 Jan;49(1):280-290. doi: 10.1002/jmri.26192. Epub 2018 May 14. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2019. PMID: 29761595
-
A prediction model based on deep learning and radiomics features of DWI for the assessment of microsatellite instability in endometrial cancer.Cancer Med. 2024 Aug;13(16):e70046. doi: 10.1002/cam4.70046. Cancer Med. 2024. PMID: 39171859 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Amin, M., Osman, M., Abdel Reheim, A. & Hassan, R. The Role of Dynamic Post Contrast Enhanced and Diffusion Weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Detection of Endometrial Carcinoma. Minia J. Med. Res.31, 322–331 (2020).
-
- Gatius, S. et al. Tumor Heterogeneity in Endometrial Carcinoma: Practical Consequences. Pathobiology85, 35–40 (2018). - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

