Changes in various forms of fibronectin in patients undergoing coronary artery bypass grafting with cardiopulmonary bypass - a prospective, observational study
- PMID: 39730478
- PMCID: PMC11681034
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-80765-9
Changes in various forms of fibronectin in patients undergoing coronary artery bypass grafting with cardiopulmonary bypass - a prospective, observational study
Abstract
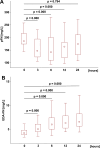
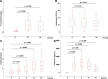
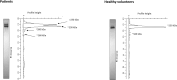
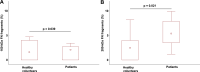
Coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) with cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB) is associated with the transient activation of a systemic inflammatory response. Fibronectin (FN), an endogenous inflammatory mediator, is a key component of the extracellular matrix. This study aimed to detect changes in cellular and plasma FN levels, as well as its potential fragmentation or FN-fibrin complex formation, in 40 patients undergoing CABG with CPB. Our results indicate that CPB was associated with changes in the levels of cellular and plasma FN and with intensified FN fragmentation. Moreover, FN-fibrin complexes were detected in all patients, indicating activation of the coagulation process during CPB. In a multivariate regression analysis, a history of arterial hypertension and CPB duration influenced plasma FN levels at 6 h (β = -0.458, p = 0.001; -0.375, p = 0.008, respectively) and 12 h (β = -0.293, p = 0.026; -0.554, p = 0.000) after surgery. Alterations in FN concentration, intensified FN degradation, and the presence of FN-fibrin complexes after surgery may suggest that these changes are related to the remodelling of the extracellular matrix resulting from cardiac surgery and the associated repair processes. The results indicate that FN has clinical potential as a marker of repair processes.
Keywords: Cardiopulmonary bypass; EDA-FN; FN-fibrin complexes; Fibronectin; Inflammation.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Ethical approval: The study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Bioethical Committee of Wroclaw Medical University (KB – 280/2016, KB – 214/2023), and informed consent was obtained from all patients (study groups) and healthy volunteers (control group).
Figures
Similar articles
-
Analysis of Soluble Molecular Fibronectin-Fibrin Complexes and EDA-Fibronectin Concentration in Plasma of Patients with Atherosclerosis.Inflammation. 2016 Jun;39(3):1059-68. doi: 10.1007/s10753-016-0336-0. Inflammation. 2016. PMID: 27022744 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of hemostasis after coronary artery bypass grafting with or without cardiopulmonary bypass.Anesth Analg. 2004 Sep;99(3):634-640. doi: 10.1213/01.ANE.0000130257.64006.5C. Anesth Analg. 2004. PMID: 15333385 Clinical Trial.
-
Neuronal and astroglial injuries in patients undergoing coronary artery bypass grafting and aortic arch replacement during hypothermic cardiopulmonary bypass.Anesth Analg. 2000 Nov;91(5):1066-72. doi: 10.1097/00000539-200011000-00005. Anesth Analg. 2000. PMID: 11049885
-
Neutrophil gelatinase associated lipocalin as a biomarker for acute kidney injury in patients undergoing coronary artery bypass grafting with cardiopulmonary bypass.Ann Vasc Surg. 2010 May;24(4):525-31. doi: 10.1016/j.avsg.2010.01.001. Epub 2010 Apr 2. Ann Vasc Surg. 2010. PMID: 20363104 Review.
-
Fibronectin and its soluble EDA-FN isoform as biomarkers for inflammation and sepsis.Adv Clin Exp Med. 2019 Nov;28(11):1561-1567. doi: 10.17219/acem/104531. Adv Clin Exp Med. 2019. PMID: 31596557 Review.
References
-
- Levi, M., van der Poll, T. & Büller, H. R. Bidirectional relation between inflammation and coagulation. Circulation109, 2698–2704. 10.1161/01.CIR.0000131660.51520.9A (2004). - PubMed
-
- Jebali, M. A. et al. Assessment of the accuracy of procalcitonin to diagnose postoperative infection after cardiac surgery. Anesthesiology107, 232–238. 10.1097/01.anes.0000271871.07395.ad (2007). - PubMed
-
- Lindsey, M. L., Mann, D. L., Entman, M. L. & Spinale, F. G. Extracellular matrix remodeling following myocardial injury. Ann. Med.35, 316–326. 10.1080/07853890310001285 (2003). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

