Construction and validation of a nomogram model to predict bronchiolitis Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia in children
- PMID: 39730508
- PMCID: PMC11681095
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-80906-0
Construction and validation of a nomogram model to predict bronchiolitis Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia in children
Abstract
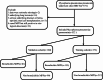
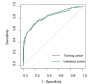
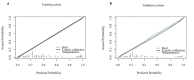
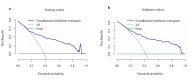
After the cancellation of COVID-19 epidemic control measures in 2023, cases of pediatric bronchiolitis caused by Mycoplasma pneumoniae (MP) have been reported successively, with some children experiencing residual bronchiolitis obliterans (BO). Currently, the diagnosis of bronchiolitis Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia (MPP) primarily relies on high-resolution computed tomography (HRCT). To establish a predictive model for bronchiolitis MPP, a retrospective analysis was conducted. The patients were randomly divided into a training cohort and a validation cohort. The nomogram model was constructed in the training cohort. Finally, the differential, calibration, and clinical applicability of the prediction model were evaluated using both the training and validation cohorts. Logistic stepwise regression analysis identified age, atopy, wheezing, hypoxemia, and pleural effusion as independent predictors of bronchiolitis MPP. These factors were used to construct a nomogram model. This nomogram model serves as a useful tool for predicting the risk of bronchiolitis MPP, which may facilitate individualized early intervention.
Keywords: Mycoplasma pneumoniae; Atopy; Bronchiolitis; Nomogram.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Ethics approval and consent to participate: The studies involving humans were approved by the Medical Ethics Committee of Xiamen University Affiliated First Hospital (institutional review board numbers: 2023-094). The studies were conducted in accordance with local legislation and institutional requirements. Written informed consent for participation in this study was provided by the participants’ legal guardians/next of kin.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- 2022YFC2704803/the National Key R&D Program "Reproductive Health and Women and Children's Health Guarantee"
- 2022YFC2704803/the National Key R&D Program "Reproductive Health and Women and Children's Health Guarantee"
- 2022YFC2704803/the National Key R&D Program "Reproductive Health and Women and Children's Health Guarantee"
- 2022YFC2704803/the National Key R&D Program "Reproductive Health and Women and Children's Health Guarantee"
- 2022YFC2704803/the National Key R&D Program "Reproductive Health and Women and Children's Health Guarantee"
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

