Distributed opinion competition scheme with gradient-based neural network in social networks
- PMID: 39730650
- PMCID: PMC11681056
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-81857-2
Distributed opinion competition scheme with gradient-based neural network in social networks
Abstract
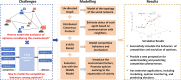
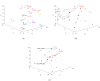
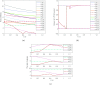
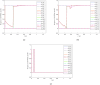
In the context of social networks becoming primary platforms for information dissemination and public discourse, understanding how opinions compete and reach consensus has become increasingly vital. This paper introduces a novel distributed competition model designed to elucidate the dynamics of opinion competitive behavior in social networks. The proposed model captures the development mechanism of various opinions, their appeal to individuals, and the impact of the social environment on their evolution. The model reveals that a subset of opinions ultimately prevails and is adopted. Key elements of social networks are quantified as parameters, with parameter variations representing the dynamics of opinions. Furthermore, a modified gradient-based neural network is designed as the evolutional law of the opinion, whose stability and convergence are confirmed by theoretical analysis. Additionally, experiments simulate real-world competitive scenarios, demonstrating practical applications for the model. This model can be widely applied to various filed in social networks, offering a new perspective for understanding and predicting competition phenomenon in complex social systems. Overall, this work provides a structured and systematic approach to understanding opinion dynamics, which greatly enhances our ability to analyze competitive behaviors and anticipate the outcomes of diverse viewpoints in social networks.
Keywords: k-winners-take-all (k-WTA); Distributed scheme; Opinion competition; Recurrent neural network (RNN); Social network.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Opinion dynamics in social networks under competition: the role of influencing factors in consensus-reaching.R Soc Open Sci. 2022 May 18;9(5):211732. doi: 10.1098/rsos.211732. eCollection 2022 May. R Soc Open Sci. 2022. PMID: 35620005 Free PMC article.
-
Opinion evolution in different social acquaintance networks.Chaos. 2017 Nov;27(11):113111. doi: 10.1063/1.5008391. Chaos. 2017. PMID: 29195305
-
Modeling and analyzing an opinion network dynamics considering the environmental factor.Math Biosci Eng. 2023 Aug 24;20(9):16866-16885. doi: 10.3934/mbe.2023752. Math Biosci Eng. 2023. PMID: 37920038
-
A novel recurrent neural network with one neuron and finite-time convergence for k-winners-take-all operation.IEEE Trans Neural Netw. 2010 Jul;21(7):1140-8. doi: 10.1109/TNN.2010.2050781. IEEE Trans Neural Netw. 2010. PMID: 20659863
-
Initialization-Based k-Winners-Take-All Neural Network Model Using Modified Gradient Descent.IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst. 2023 Aug;34(8):4130-4138. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2021.3123240. Epub 2023 Aug 4. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst. 2023. PMID: 34752408
References
-
- Geng, L., Yang, S., Wang, K., Zhou, Q. & Geng, L. Modeling public opinion dissemination in a multilayer network with SEIR model based on real social networks. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell.125, 106719 (2023).
-
- Wei-Dong, H., Qian, W. & Jie, C. Tracing public opinion propagation and emotional evolution based on public emergencies in social networks. Int. J. Comput. Commun. Control13, 129–142 (2018).
-
- Bimpikis, K., Ozdaglar, A. & Yildiz, E. Competitive targeted advertising over networks. Oper. Res.64, 705–720 (2016).
-
- Lang, N., Wang, L. & Zha, Q. Targeted allocation of marketing resource in networks based on opinion dynamics. Mathematics10, 394 (2022).
-
- Zhao, Y., Kou, G., Peng, Y. & Chen, Y. Understanding influence power of opinion leaders in e-commerce networks: An opinion dynamics theory perspective. Inf. Sci.426, 131–147 (2018).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

