A novel biomarker of COVID-19: MMP8 emerged by integrated bulk RNAseq and single-cell sequencing
- PMID: 39730651
- PMCID: PMC11680813
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-82227-8
A novel biomarker of COVID-19: MMP8 emerged by integrated bulk RNAseq and single-cell sequencing
Abstract
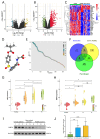
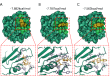
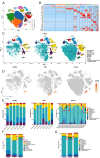
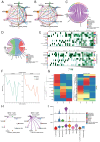
COVID-19 has been emerging as the most influential illness which has caused great costs to the heath of population and social economy. Sivelestat sodium (SS) is indicated as an effective cure for lung dysfunction, a characteristic symptom of COVID-19 infection, but its pharmacological target is still unclear. Therefore, a deep understanding of the pathological progression and molecular alteration is an urgent issue for settling the diagnosis and therapy problems of COVID-19. In this study, the bulk ribonucleic acid sequencing (RNA-seq) data of healthy donors and non-severe and severe COVID-19 patients were collected. Then, target differentially expressed genes (DEGs) were screened through integrating sequencing data and the pharmacological database. Besides, with the help of functional and molecular interaction analyses, the potential effect of target gene alteration on COVID-19 progression was investigated. Single-cell sequencing was performed to evaluate the cell distribution of target genes, and the possible interaction of gene-positive cells with other cells was explored by intercellular ligand-receptor pattern analysis. The results showed that matrix metalloproteinase 8 (MMP8) was upregulated in severe COVID-19 patients, which was also identified as a targeting site to SS. Additionally, MMP8 took a core part in the regulatory interaction network of the screened DEGs in COVID-19 and was dramatically correlated with the inflammatory signaling pathway. The further investigations indicated that MMP8 was mainly expressed in myelocytes with a high degree of heterogeneity. MMP8-positive myelocytes interacted with other cell types through RETN-TLR4 and RETN-CAP1 ligand-receptor patterns. These findings emphasize the important role of MMP8 in COVID-19 progression and provide a potential therapeutic target for COVID-19 patients.
Keywords: COVID-19; Cell-to-cell communication; MMP8; RNA sequencing; Single-cell sequencing.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Ethical approval and consent to participate: Our study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Ethics Committee, Shaanxi Provincial People’s Hospital (no. SPPH-LLBG-17-3_2). Consent for publication: Not applicable.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

