Comparative analysis of antifungal activity of Rhazya stricta ethanolic extracts and biogenic silver nanoparticles against pathogenic fungi
- PMID: 39730698
- PMCID: PMC11681160
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-82015-4
Comparative analysis of antifungal activity of Rhazya stricta ethanolic extracts and biogenic silver nanoparticles against pathogenic fungi
Abstract
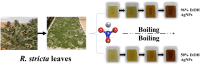
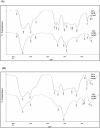
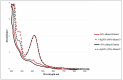
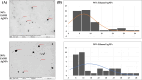
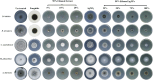
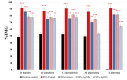
Rhazya stricta, a perennial shrub native to the Middle East and South Asia, has been used in traditional medicine for various therapeutic purposes, including antimicrobial action. The current study aimed to compare the antifungal properties of 96% and 50% ethanolic extracts of R. stricta leaves and their biogenic silver nanoparticles (AgNPs). The phytochemical constituents of both extracts were analyzed by Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (GC-MS). The AgNPs were characterized using FTIR, UV-Vis spectroscopy, DLS, and TEM, confirming bioactive chemicals' effective production and existence. The antifungal efficacy was tested on five pathogenic fungi: Drechslera halodes, Drechslera tetramera, Macrophomina phaseolina, Alternaria alternata, and Curvularia australiensis. The 96% ethanol extract inhibited fungal growth the most, with D. halodes, C. australiensis, and A. alternata all experiencing almost 100% inhibition. AgNPs also showed strong antifungal efficacy, with those generated from 96% ethanol extract outperforming those from 50% ethanol extract. This study highlights the potential of R. stricta extracts and their biogenic AgNPs as environmentally friendly antifungal agents, which supports their use in long-term antimicrobial therapy.
Keywords: Rhazya Stricta; Antifungal activities; Ethanolic extracts; Silver nanoparticles.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Baeshen, M. N., Khanm, R., Bora, R. S. & Baeshen, N. A. Therapeutic potential of the folkloric medicinal plant Rhazya stricta. Biol. Syst. Open Access5, 1. 10.4172/2329-6577.1000151 (2015). - DOI
-
- Saif, A. Phytochemical, antioxidant, and antimicrobial effects of methanolic leaf extract of Rhazya stricta decne. Int. J. Res. Med. Sci.10, 293–300. (2022). - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

