Neratinib enhances the efficacy of CDK4/6 inhibitor plus endocrine therapy in HR+/HER2-low breast cancer cell line ZR-75-1 via hsa-miR-23a-5p
- PMID: 39730704
- PMCID: PMC11680982
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-82137-9
Neratinib enhances the efficacy of CDK4/6 inhibitor plus endocrine therapy in HR+/HER2-low breast cancer cell line ZR-75-1 via hsa-miR-23a-5p
Abstract
HR+/HER2-low breast cancer is a significant subgroup of conventional HR+/HER2-negative breast cancer, and combination of CDK4/6 inhibitor and endocrine therapy is the standard first-line and second-line treatments for advanced HR+/HER2-low breast cancer. Nevertheless, it remains uncertain whether HER2 signaling affects the effectiveness of CDK4/6 inhibitor administered in combination with endocrine therapy for HR+/HER2-low breast cancer and suitable intervention measures. This study revealed poor efficacy for CDK4/6 inhibitor combined with endocrine therapy for HR+/HER2-low breast cancer in vitro and in vivo models. Secondly, suppression of HER2 gene expression in HR+/HER2-low breast cancer cells resulted in significantly improved efficacy for CDK4/6 inhibitor combined with endocrine therapy. Furthermore, the anti-HER inhibitor neratinib was administered to enhance the effectiveness of CDK4/6 inhibitor combined with endocrine therapy in HR+/HER2-low breast cancer by inhibiting the HER2 pathway and lowering HER2 mRNA expression. Strikingly, neratinib reversed the efficacy of CDK4/6 inhibitor and endocrine therapy by reducing HER2 mRNA stability in HR+/HER2-low breast cancer through the interaction of HER2 3'-UTR region with hsa-miR-23a-5p. Even after reducing neratinib dosage to the standard 1/2 dose (20 mg/kg), it remained highly effective and well-tolerated. This study provides a viable and well-tolerated triple combination therapy for clinical HR+/HER2-low breast cancer.
Keywords: CDK4/6 inhibitor; Endocrine therapy; HER2 mRNA stability; HR+/HER2-low; Hsa-miR-23a-5p; Neratinib.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Ethical approval: This study was conducted according to ARRIVE guidelines 2.0. Liushan Chen, Lingling Ye, and Yuqi Liang are co-first authors. Yingchao Wu, Qianqian Guo, and Qianjun Chen are co-corresponding authors.
Figures
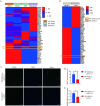
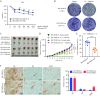


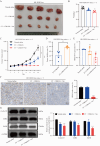

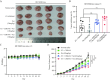
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- KC2022-ZZ-0091-1/Science and Technology Innovation Medical Development Foundation of Beijing
- KC2021-ZZ-0010-9/Science and Technology Innovation Medical Development Foundation of Beijing
- 2022A1515110859/Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation of Guangdong Province
- 82274513/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- HQL2024PZ023/Project supported by the Incubation Program for the Science and Technology Development of Chinese Medicine Guangdong Laboratory
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

