Electrochemical polymerized DL-phenylalanine modified carbon nanotube sensor for the selective and sensitive determination of caffeic acid with riboflavin
- PMID: 39730719
- PMCID: PMC11681202
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-82011-8
Electrochemical polymerized DL-phenylalanine modified carbon nanotube sensor for the selective and sensitive determination of caffeic acid with riboflavin
Abstract
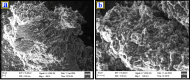
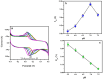
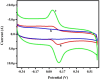
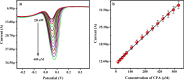
In this study, DL-phenylalanine modified with a multiwall carbon nanotube paste electrode is used as advanced electrochemical sensor for analysing of 0.1 mM caffeic acid (CFA) with simultaneous detection of riboflavin (RFN). The developed sensors include electrochemically polymerized DL-phenylalanine (DL-PA) modified multiwall carbon nanotube paste electrode [DL-PAMMCNTPE] and bare multiwall carbon nanotube paste electrode [BMCNTPE]. The increasing stability in the developed electrochemical sensor for the quantification of CFA is highlighted in detail, along with its characterization using voltammetric techniques such as electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS), cyclic voltammetry (CV), differential pulse voltammetry (DPV), and linear Sweep Voltammetry (LSV). Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) technique was used to studied the structural analysis of BMCNTPE and DL-PAMMCNTPE surface. The investigation of 0.1 mM CFA in 0.2 M phosphate buffered solution (PBS) using a 7.0 pH at 0.1 V/s scan rate was highlighted using DL-PAMMCNTPE, which shows good electrochemical responses compared to BMCNTPE. This work characterizes the voltammetric responses by inspecting the pH effect, scan rate effect, and concentration difference of CFA at the DL-PAMMCNTPE surface. The CFA responses specify that the scan rate progress is adsorption controlled. The concentration of CFA detection was started from 20 μM to 600 μM using DPV method, with lower limit of detection (LOD) of 0.280 μM and limit of quantification (LOQ) of 0.936 μM. And for CV method concentration range 20 to 550 μM, with LOD of 0.198 μM and LOQ of 0.702 μM. Furthermore, the developed electrochemical sensor responses are shows good stability, repeatability, and reproducibility, for CFA. The analytical applicability of CFA in apple juice and coffee powder samples was also evaluated.
Keywords: Caffeic acid; DL-phenylalanine; Electrochemical analyser; Multiwall carbon nanotube paste sensor; Voltammetry.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures







References
-
- Xu, X. et al. Carbon dots coated with molecularly imprinted polymers: A facile bioprobe for fluorescent determination of caffeic acid. J. Colloid Interface Sci.529, 568–574 (2018). - PubMed
-
- Li, J. et al. Facile synthesis of MnO2-embedded flower-like hierarchical porous carbon microspheres as an enhanced electrocatalyst for sensitive detection of caffeic acid. Anal. Chim. Acta.985, 155–165 (2017). - PubMed
-
- Ramki, S. et al. Voltammetric determination of caffeic acid using Co3O4 microballs modified screen-printed carbon electrode. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci.13, 1241–1249 (2018).
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

