The effect of early-onset sepsis on retinopathy of prematurity in extremely premature infants based on propensity score matching
- PMID: 39730752
- PMCID: PMC11680759
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-81905-x
The effect of early-onset sepsis on retinopathy of prematurity in extremely premature infants based on propensity score matching
Abstract
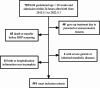
To investigate the effects of early-onset sepsis (EOS) on retinopathy of prematurity (ROP) in extremely premature infants (EPIs) by using propensity score matching (PSM). Clinical data of 591 EPIs admitted to NICU, Senior Department of Pediatric, PLA General Hospital from May 1, 2015 to May 1, 2022 were retrospectively analyzed. They were divided into an EOS group and a non-EOS group according to whether they had confirmed EOS or not. The incidence of ROP and severe ROP was compared between the two groups using the 1:1 PSM method. Of the 591 EPIs, 57 (9.6%) fell in the EOS group and the remaining 534 in the non-EOS group. There were statistical differences in artificial conception, cesarean section, bronchopulmonary dysplasia, duration of invasive mechanical ventilation, days of oxygen use, amniotic fluid contamination, and premature rupture of membranes between the two groups (all P < 0.05), and then match these variables as covariates. Before matching, the incidence of ROP and severe ROP in the EOS group was higher than that in the non-EOS group [ROP: (35/57)61.4% vs. (224/534)41.9%, OR 2.202, 95% CI 1.257 to 3.856, P = 0.005; severe ROP: (25/57)43.9% vs. (149/534)27.9%, OR 2.019, 95% CI 1.157 to 3.521, P = 0.012], and after matching all covariables were well matched (all P > 0.05). Of the 57 cases in the EOS group, 51 were successfully matched, in which the incidence of severe ROP was higher than that in the non-EOS group [47.1% (24/51) vs. 27.5% (14/51), OR 2.349,95% CI 1.030 to 5.360, P < 0.05]. There was no significant difference in the incidence of ROP between the two groups [62.7% (32/51) vs. 49.0% (25/51), OR 1.752,95% CI 0.795 to 3.858, P > 0.05]. EOS didn't seem to increase the incidence of ROP in EPIs, but was associated with an increase in the degree of ROP lesions. The progression of fundus lesions in EPIs with EOS during hospitalization should be closely monitored.
Keywords: Complications; Early-onset sepsis, neonatal; Infants, extremely premature; Propensity score; Retinopathy of prematurity.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous