Bioinformatics based exploration of the anti-NAFLD mechanism of Wang's empirical formula via TLR4/NF-κB/COX2 pathway
- PMID: 39730994
- PMCID: PMC11673956
- DOI: 10.1186/s10020-024-01022-3
Bioinformatics based exploration of the anti-NAFLD mechanism of Wang's empirical formula via TLR4/NF-κB/COX2 pathway
Abstract
Background: Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) has developed as a leading public wellness challenge as a result of changes in dietary patterns. Unfortunately, there is still a lack of effective pharmacotherapy methods for NAFLD. Wang's empirical formula (WSF) has demonstrated considerable clinical efficacy in treating metabolic disorders for years. Nevertheless, the protective effect of WSF against NAFLD and its underlying mechanism remains poorly understood.
Methods: The NAFLD model was established using a 17-week high-sucrose and high-fat (HSHF) diet with 32 ICR mice. In assessing the therapeutic efficacy of WSF on NAFLD, we detected changes in body weight, viscera weight, biomarkers of glycolipid metabolism in serum and liver, transaminase levels and histopathology of liver with H&E and Oil Red O staining after oral administration. The chemical components in WSF were extensively identified and gathered utilizing the HPLC-Q-TOF/MS system, database mining from HMDB, MassBank, and TCMSP databases, alongside literature searches from CNKI, Wanfang and VIP databases. The forecast of network pharmacology approach was then utilized to investigate the probable mechanisms by which WSF improves NAFLD based on the performance of prospective target identification and pathway enrichment analysis. Besides, molecular docking was also conducted for the verification of combination activities between active components of WSF and core proteins related to NAFLD. In final, validation experiments of obtained pathways were conducted through ELISA, immunohistochemistry (IHC), and western blot (WB) analysis.
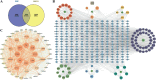
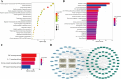
Results: Pharmacodynamic outcomes indicated that WSF intervention effectively mitigated obesity, fat accumulation in organs, lipid metabolism disorders, abnormal transaminase levels and liver pathology injury in NAFLD mice (P < 0.05, 0.01). A total of 72 existent ingredients of WSF were acquired by HPLC-Q-TOF/MS and database, and 254 common targets (11.6% in total targets) of NAFLD and WSF were identified. Network pharmacology revealed that WSF presses NAFLD via modulating TNF, IL6, AKT1, IL1B, PTGS2 (COX2), and other targets, and the probable pathways were primarily inflammatory signaling pathways, as confirmed by molecular docking. Molecular biology experiments further conformed that WSF could decrease levels of inflammatory factors like IL-1β, IL-6 and TNF-α (P < 0.01) and expression of TLR4, NF-κB and COX-2 (P < 0.05, 0.01) in the liver.
Conclusion: WSF treatment effectively protects against lipid metabolism disorders and liver inflammation injury in HSHF diet-induced NAFLD mice, and its molecular mechanism might be via suppressing the TLR4/NF-κB/COX-2 inflammatory pathway to reduce the release of inflammatory cytokines in the liver.
Keywords: Bioinformatics; HPLC-Q-TOF/MS; Liver inflammation; Network pharmacology; Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease; Wang’s empirical formula.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: The Animal Ethics Committee of the Zhejiang University of Technology ratified the experiment plan (No. 20211119097, 19–11-2021). Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures







References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

