Advancements in MRSA treatment: the role of berberine in enhancing antibiotic therapy
- PMID: 39731013
- PMCID: PMC11674092
- DOI: 10.1186/s12866-024-03692-9
Advancements in MRSA treatment: the role of berberine in enhancing antibiotic therapy
Abstract
Background: Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) is a significant public health problem. This study investigated the antimicrobial properties and mechanisms of berberine (BBR), a plant alkaloid, against MRSA, evaluating its potential to enhance antibiotic therapy.
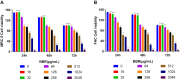
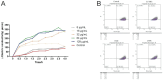
Results: Berberine only demonstrated variable but significant inhibitory effects on 50 clinical MRSA strains. When combined with antibiotics, synergistic effects were observed only with amikacin in 6 of the 50 MRSA strains. BBR disrupted MRSA cell wall integrity, leading to leakage of cellular contents. Network pharmacology analysis revealed that BBR targets multiple pathways essential for bacterial survival.
Conclusion: The study confirmed the potent antimicrobial activity of berberine against MRSA and its capability to act synergistically with traditional antibiotics. Berberine's impact on cell wall integrity and bacterial survival pathways highlights its potential as an adjunct therapy in MRSA treatment.
Keywords: Berberine; Cell wall damage; Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus; Minimum inhibitory concentration; Network pharmacology.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: This study, isolating MRSA strains from clinical patient samples, adhered to strict ethical guidelines for clinical research. The study strictly followed the Declaration of Helsinki, and ethics approval was obtained from the Ethics Committee of Shanghai Eighth People’s Hospital (Approval Number: 2023-058-18). All participating patients provided written informed consent. Conflict of interest: The author declares no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
The combined antibacterial effects of sodium new houttuyfonate and berberine chloride against growing and persistent methicillin-resistant and vancomycin-intermediate Staphylococcus aureus.BMC Microbiol. 2020 Oct 19;20(1):317. doi: 10.1186/s12866-020-02003-2. BMC Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 33076836 Free PMC article.
-
Berberine inhibits the tarO gene to impact MRSA cell wall synthesis.Sci Rep. 2025 Feb 26;15(1):6927. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-91724-3. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40011701 Free PMC article.
-
Potent in vitro synergism of fusidic acid (FA) and berberine chloride (BBR) against clinical isolates of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA).World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2014 Nov;30(11):2861-9. doi: 10.1007/s11274-014-1712-2. Epub 2014 Aug 10. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2014. PMID: 25108628
-
Combating multidrug-resistant (MDR) Staphylococcus aureus infection using terpene and its derivative.World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2024 Dec 4;40(12):402. doi: 10.1007/s11274-024-04190-w. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 39627623 Review.
-
Correlation Between Biofilm Formation and Antibiotic Resistance in MRSA and MSSA Isolated from Clinical Samples in Iran: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Microb Drug Resist. 2020 Sep;26(9):1071-1080. doi: 10.1089/mdr.2020.0001. Epub 2020 Mar 10. Microb Drug Resist. 2020. PMID: 32159447
Cited by
-
Mechanistic studies on the effect of berberine on methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus drug resistance through modulation of wall teichoteic acid.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 17;15(1):26003. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-11226-0. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40676072 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Henriquez E, Fatima N, Sayabugari R, et al. Transesophageal Echocardiography vs. Transthoracic Echocardiography for Methicillin-Sensitive Staphylococcus aureus and Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Endocarditis. Cureus. 2023;15(6):e39996. 10.7759/cureus.39996. Published 2023 Jun 5. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chen TY, Ge YL, Liu XW, et al. Zhonghua Yu Fang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2020;54(8):849–53. 10.3760/cma.j.cn112150-20190819-00669 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

