Advancements in MRSA treatment: the role of berberine in enhancing antibiotic therapy
- PMID: 39731013
- PMCID: PMC11674092
- DOI: 10.1186/s12866-024-03692-9
Advancements in MRSA treatment: the role of berberine in enhancing antibiotic therapy
Abstract
Background: Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) is a significant public health problem. This study investigated the antimicrobial properties and mechanisms of berberine (BBR), a plant alkaloid, against MRSA, evaluating its potential to enhance antibiotic therapy.
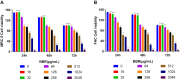
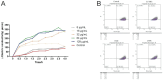
Results: Berberine only demonstrated variable but significant inhibitory effects on 50 clinical MRSA strains. When combined with antibiotics, synergistic effects were observed only with amikacin in 6 of the 50 MRSA strains. BBR disrupted MRSA cell wall integrity, leading to leakage of cellular contents. Network pharmacology analysis revealed that BBR targets multiple pathways essential for bacterial survival.
Conclusion: The study confirmed the potent antimicrobial activity of berberine against MRSA and its capability to act synergistically with traditional antibiotics. Berberine's impact on cell wall integrity and bacterial survival pathways highlights its potential as an adjunct therapy in MRSA treatment.
Keywords: Berberine; Cell wall damage; Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus; Minimum inhibitory concentration; Network pharmacology.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: This study, isolating MRSA strains from clinical patient samples, adhered to strict ethical guidelines for clinical research. The study strictly followed the Declaration of Helsinki, and ethics approval was obtained from the Ethics Committee of Shanghai Eighth People’s Hospital (Approval Number: 2023-058-18). All participating patients provided written informed consent. Conflict of interest: The author declares no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Henriquez E, Fatima N, Sayabugari R, et al. Transesophageal Echocardiography vs. Transthoracic Echocardiography for Methicillin-Sensitive Staphylococcus aureus and Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Endocarditis. Cureus. 2023;15(6):e39996. 10.7759/cureus.39996. Published 2023 Jun 5. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chen TY, Ge YL, Liu XW, et al. Zhonghua Yu Fang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2020;54(8):849–53. 10.3760/cma.j.cn112150-20190819-00669 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

