Diagnostic accuracy of metagenomic next-generation sequencing in pulmonary tuberculosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 39731100
- PMCID: PMC11674177
- DOI: 10.1186/s13643-024-02733-8
Diagnostic accuracy of metagenomic next-generation sequencing in pulmonary tuberculosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Metagenomic next-generation sequencing (mNGS) has emerged as a promising tool in clinical practice due to its unbiased approach to pathogen detection. Its diagnostic performance in pulmonary tuberculosis (PTB), however, remains to be fully evaluated.
Objective: This study aims to systematically review and Meta-analyze the diagnostic accuracy of mNGS in patients with PTB.
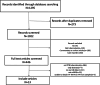
Methods: We conducted a literature search in PubMed (MEDLINE), Web of Science, Cochrane, and EMBASE databases, including studies published up to 2024. Studies comparing the diagnostic accuracy of mNGS with other methods such as Xpert-MTB/RIF and Mycobacteria tuberculosis (MTB) culture using bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF), sputum, and lung biopsy tissue were included. Preclinical studies, review articles, editorials, conference abstracts, and book chapters were excluded. Statistical analysis was performed using Rev-man5, R package metabias, and Stata software.
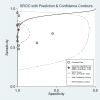
Results: Thirteen studies met the inclusion criteria and were included in the meta-analysis. The pooled sensitivity and specificity of mNGS for PTB were 83% (95% CI: 69-91%) and 99% (95% CI: 92-100%), respectively. Subgroup analyses revealed that in BALF, mNGS demonstrated a pooled sensitivity of 73% (95% CI: 61-82%) and specificity of 98% (95% CI: 92-100%); in the sputum, the pooled sensitivity was 60% (95% CI: 38-87%) with a specificity of 99% (95% CI: 96-100%); and in the lung biopsy tissue, the pooled sensitivity was 71% (95% CI: 38-95%) and the specificity was 98% (95% CI: 93-100%). For Xpert-MTB/RIF, the pooled sensitivity and specificity were 72% (95% CI: 53-85%) and 100% (95%CI: 100-100%), respectively. Subgroup analyses demonstrated that in BALF, Xpert-MTB/RIF exhibited a pooled sensitivity of 69% (95% CI: 53-81%) and a specificity of 100% (95% CI: 77-100%). The pooled sensitivity and specificity of mycobacteria culture were 50% (95% CI: 36-64%) and 100% (95% CI: 83-100%), respectively. Subgroup analyses indicated that in BALF, the pooled sensitivity of mycobacteria culture was 44% (95% CI: 37-52%) with a specificity of 100% (95% CI: 8-100%); in the sputum, the pooled sensitivity was 42% (95% CI: 21-65%) and the specificity was 100% (95% CI: 100-100%). When combining mNGS with Xpert-MTB/RIF, the pooled sensitivity and specificity were 79% (95% CI: 40-97%) and 98% (95% CI: 95-100%), respectively.
Conclusion: mNGS demonstrates similar diagnostic accuracy to Xpert-MTB/RIF in PTB and outperforms mycobacteria culture in terms of sensitivity. Furthermore, mNGS exhibits good detection capabilities across various PTB clinical samples.
Systematic review registration: PROSPERO CRD42023427586.
Keywords: Bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF); Diagnosis; Metagenomic next-generation sequencing (mNGS); Pulmonary tuberculosis (PTB); Xpert-MTB/RIF.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: An ethics statement is not applicable because this study is based exclusively on the published literature. Competing interests: The authors reported no conflict of interest in the work.
Figures











Similar articles
-
Xpert MTB/RIF Ultra assay for tuberculosis disease and rifampicin resistance in children.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Sep 6;9(9):CD013359. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013359.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36065889 Free PMC article.
-
Xpert® MTB/RIF assay for extrapulmonary tuberculosis and rifampicin resistance.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Aug 27;8(8):CD012768. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012768.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Jan 15;1:CD012768. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012768.pub3. PMID: 30148542 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Xpert® MTB/RIF assay for pulmonary tuberculosis and rifampicin resistance in adults.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013 Jan 31;(1):CD009593. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009593.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014 Jan 21;(1):CD009593. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009593.pub3. PMID: 23440842 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Lateral flow urine lipoarabinomannan assay for detecting active tuberculosis in HIV-positive adults.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 May 10;2016(5):CD011420. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011420.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27163343 Free PMC article.
-
Value of Xpert MTB/RIF Using Bronchoalveolar Lavage Fluid for the Diagnosis of Pulmonary Tuberculosis: a Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.J Clin Microbiol. 2021 Mar 19;59(4):e02170-20. doi: 10.1128/JCM.02170-20. Print 2021 Mar 19. J Clin Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33177121 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Diagnostic Delay Among Pulmonary Tuberculosis Patients Before, During and After COVID-19 Pandemic in Yichang City, China: A Longitudinal Study Based on Tuberculosis Surveillance Data.J Epidemiol Glob Health. 2025 May 26;15(1):74. doi: 10.1007/s44197-025-00419-5. J Epidemiol Glob Health. 2025. PMID: 40418412 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Harding E. WHO global progress report on tuberculosis elimination. The Lancet Respiratory Medicine. 2020 2020/01/01/;8(1):19. 10.1016/S2213-2600(19)30418-7. - PubMed
-
- Floyd K, Glaziou P, Zumla A, Raviglione M. The global tuberculosis epidemic and progress in care, prevention, and research: an overview in year 3 of the End TB era. The Lancet Respiratory Medicine. 2018 2018/04/01/;6(4):299–314. 10.1016/S2213-2600(18)30057-2. - PubMed
-
- Jain D, Ghosh S, Teixeira L, Mukhopadhyay S. Pathology of pulmonary tuberculosis and non-tuberculous mycobacterial lung disease: Facts, misconceptions, and practical tips for pathologists. Seminars in Diagnostic Pathology. 2017 2017/11/01/;34(6):518–29. 10.1053/j.semdp.2017.06.003. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

