Progress of CCL20-CCR6 in the airways: a promising new therapeutic target
- PMID: 39731176
- PMCID: PMC11681768
- DOI: 10.1186/s12950-024-00427-5
Progress of CCL20-CCR6 in the airways: a promising new therapeutic target
Erratum in
-
Correction: Progress of CCL20-CCR6 in the airways: a promising new therapeutic target.J Inflamm (Lond). 2025 Jan 13;22(1):2. doi: 10.1186/s12950-025-00428-y. J Inflamm (Lond). 2025. PMID: 39806407 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
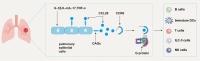
The chemokine CCL20, a small cytokine that belongs to the C-C chemokine family, interacts with its homologous receptor CCR6, which is expressed on wide range of cell types. According to current research, the CCL20-CCR6 has been established as acritical player in a diverse range of inflammatory, oncogenic, and autoimmune diseases. Within the respiratory system, CCL20-CCR6 demonstrates heightened expression in conditions such as allergic asthma, chronic airway inflammation, non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and other respiratory diseases, which is conducive to the inflammatory mediators recruitment and tumor microenvironment remodeling. Numerous studies have demonstrated that therapeutic interventions targeting CCL20 and CCR6, including antibodies and antagonists, have the potential to mitigate disease progression. Despite the promising research prospects surrounding the CCL20-CCR6 chemokine axis, the precise mechanisms underlying its action in respiratory diseases remain largely elusive. In this review, we delve into the potential roles of the CCL20-CCR6 axis within the respiratory system by synthesizing and analyzing current research findings. Our objective is to provide a comprehensive understanding of the CCL20-CCR6 axis and its implications for respiratory health and disease. And we aspire to propel research endeavors in this domain and furnish valuable insights for the development of future therapeutic strategies.
Keywords: CCL20; CCR6; Immunoreaction; Inflammation; Respiratory system.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Lin S, et al. PM(2.5) and its components and respiratory disease healthcare encounters - unanticipated increased exposure-response relationships in recent years after environmental policies. Environ Pollut. 2024;360:124585. - PubMed
-
- Ono SJ, et al. Chemokines: roles in leukocyte development, trafficking, and effector function. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2003;111(6):1185–99 quiz 1200. - PubMed
-
- Reibman J, et al. Airway epithelial cells release MIP-3alpha/CCL20 in response to cytokines and ambient particulate matter. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2003;28(6):648–54. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

