The Efficacy of Liquid Biopsy of Total cfDNA for Predicting Systemic Metastasis in Japanese Patients With Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma
- PMID: 39731308
- PMCID: PMC12038226
- DOI: 10.1002/hed.28054
The Efficacy of Liquid Biopsy of Total cfDNA for Predicting Systemic Metastasis in Japanese Patients With Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Abstract
Background: The use of liquid biopsy of total cell-free DNA (cfDNA) to identify otherwise undetectable cancers has attracted interest; however, its efficacy remains unknown. We explored whether analysis using total cfDNA is efficacious for Japanese patients with oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC).
Methods: We collected total cfDNA from nine patients with OSCC preoperatively, 1 month postoperatively, and every 3 months thereafter to analyze this association. We used a target DNA sequence for genetic mutation analysis of tumor tissues collected from 33 patients, including the aforementioned nine patients.
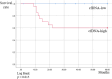
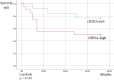
Results: Patients with good disease control showed negligible changes in preoperative and postoperative total cfDNA concentrations. A rapid increase in total cfDNA concentration was observed in patients who developed systemic metastases. Patients whose tumor tissue DNA showed genetic mutations had the same mutations in preoperative circulating tumor DNA.
Conclusions: Our data suggested that analyzing total cfDNA is efficacious for patients with OSCC.
Keywords: head and neck cancer; liquid biopsy; oral squamous cell carcinoma; systemic metastasis; total cfDNA.
© 2024 The Author(s). Head & Neck published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
- 19H03855/Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research from the Japan Society of the Promotion of Science: B,KAKENHI
- 18K17239/Grants-in-Aid for Young Scientists from the Japan Society of the Promotion of Science: KAKENHI
- 22K17022/Grants-in-Aid for Young Scientists from the Japan Society of the Promotion of Science: KAKENHI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

