Primary hepatic epithelioid hemangioendothelioma: a case report
- PMID: 39731438
- PMCID: PMC11686786
- DOI: 10.1177/03000605241306649
Primary hepatic epithelioid hemangioendothelioma: a case report
Abstract
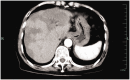
Epithelioid hemangioendothelioma is a low-grade malignant tumor of vascular origin. The rarity of hepatic epithelioid hemangioendothelioma (HEHE) makes the diagnosis and treatment of this entity challenging. We report a case of a 69-year-old female patient who suffered from HEHE and complained of abdominal distension pain with dizziness and appetite loss for more than half a month. Enhanced computed tomography of the upper abdomen indicated multiple space-occupying lesions in the liver. The pathological results of color ultrasound puncture suggested HEHE. We performed transcatheter arterial chemoembolization and relevant examinations according to the patient's condition and their choice. We followed the patient for 5 years and found that she developed recurrent intrahepatic metastasis of the tumor. Computed tomography was performed again after 3 months of treatment with anlotinib and the tumor did not show any progression. HEHE is a relatively rare hepatic malignant tumor derived from vascular endothelial cells, with a low incidence, atypical clinical manifestations, and a difficult diagnosis that can only be confirmed with pathological results. Currently, appropriate treatment methods should be selected according to the specific conditions of the patient.
Keywords: Hepatic epithelioid hemangioendothelioma; anlotinib; glucose metabolism; liver transplantation; metastasis; transcatheter arterial chemoembolization.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of conflicting interestThe authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures
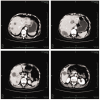
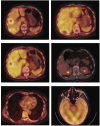
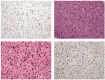
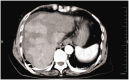
References
-
- Chahrour MA, Khachfe HH, Habib JR, et al. Treatment and Prognosis of Hepatic Epithelioid Hemangioendothelioma: A SEER Database Analysis. World J Surg 2021; 45: 2886–2894. - PubMed
-
- Hertl M, Cosimi AB. Liver transplantation for malignancy. Oncologist 2005; 10: 269–281. - PubMed
-
- Yurkiewicz IR, Zhou M, Ganjoo KN, et al. Management Strategies for Patients With Epithelioid Hemangioendothelioma: Charting an Indolent Disease Course. Am J Clin Oncol 2021; 44: 419–422. - PubMed
-
- Mehrabi A, Kashfi A, Fonouni H, et al. Primary malignant hepatic epithelioid hemangioendothelioma: a comprehensive review of the literature with emphasis on the surgical therapy. Cancer 2006; 107: 2108–2121. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

