Tuberculous osteo-arthritis unmasked through unusual elbow swelling: A case report
- PMID: 39731801
- PMCID: PMC11741017
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijscr.2024.110759
Tuberculous osteo-arthritis unmasked through unusual elbow swelling: A case report
Abstract
Introduction and importance: Tuberculous osteoarthritis, a rare condition affecting the elbow in 1-5 % of cases, poses diagnostic challenges due to its subtle clinical presentation, often resulting in delayed diagnosis. Herein, we present a case of tuberculous osteoarthritis involving the elbow joint. Our aim is to underscore the complexities associated with diagnosing this condition and to emphasize the critical importance of early recognition and appropriate management strategies for optimal patient outcomes.
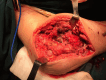
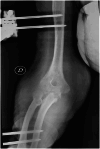
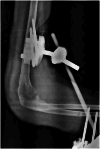
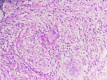
Case presentation: A 44-year-old Tunisian woman presented with a year-long history of painful right elbow swelling, systemic symptoms, and purulent drainage. Physical examination revealed a swollen, erythematous elbow with limited mobility. Radiographs showed periarticular osteolysis and subluxation, and Mycobacterium tuberculosis was cultured from the purulent drainage. The patient underwent open arthrotomy, synovectomy, joint irrigation, external fixation, and immobilization. Histopathology confirmed tuberculosis. She started a 12-month anti-tuberculous treatment and rehabilitation plan but was lost to follow-up due to socioeconomic difficulties.
Clinical discussion: This case underscores the intricate diagnostic challenges of tuberculous osteoarthritis, emphasizing the necessity of a comprehensive assessment for precision in diagnosis. Timely intervention plays a pivotal role in averting joint deterioration and securing favorable results, especially in regions with high endemicity.
Conclusions: Early recognition and management of tuberculous osteoarthritis are vital for preserving joint function. Maintaining a high suspicion for tuberculosis in cases of unusual joint symptoms is key to timely diagnosis and effective treatment, leading to improved patient care and outcomes.
Keywords: Elbow; Infection; Osteo-arthritis pathology; Tuberculosis.
Copyright © 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement None declared.
Figures





References
-
- Geneva: World Health Organization; 2017. Global TB Rep. 2017.
-
- Sharma S.K., Mohan A., Kohli M. Extrapulmonary tuberculosis. Expert Rev. Respir. Med. 2021;15(7):931–948. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

