The impact of rhubarb (Rheum Ribes L.) juice-based marinade on the quality characteristics and microbial safety of chicken breast fillets during refrigerated storage
- PMID: 39731871
- PMCID: PMC11742364
- DOI: 10.1016/j.psj.2024.104719
The impact of rhubarb (Rheum Ribes L.) juice-based marinade on the quality characteristics and microbial safety of chicken breast fillets during refrigerated storage
Abstract
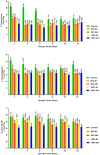
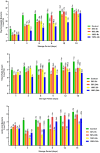
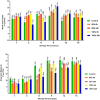
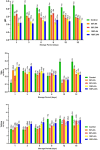
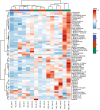
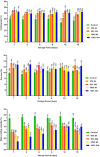
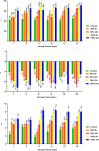
Acidic marinades are commonly used to improve the quality meat products. However, no study has been performed to determine the effects of rhubarb juice as a marinating liquid on the quality parameters of chicken breast fillets. The aim of the present study was to identify the bioactive compounds (organic acids, polyphenols, and volatiles) in the juice of rhubarb and to determine the effect of rhubarb juice as a marinade on the microbiological (total viable count, psychrotrophs, lactic acid bacteria, sulfate-reducing anaerobes, and yeast-molds) and physico-chemical properties (drip loss, cooking loss, water holding capacity, pH, color, malondialdehyde, total volatile base nitrogen, and texture profiles), sensory attributes, and microbial safety (Escherichia coli O157:H7, Salmonella Typhimurium, and Listeria monocytogenes) of chicken breast fillets during a 15-day refrigerated storage. The experiment included five groups: a control (no treatment), and marinated groups treated with 50 % and 100 % rhubarb juice for 6 and 24 h. The application of a rhubarb juice-based marinade (100 % for 24 h) resulted in a significant decrease in the number of E. coli O157:H7, S. Typhimurium and L. monocytogenes by 1.67 to 2.60 log10 cfu/g compared to the control group (P < 0.05). In addition, this marinade significantly reduced the growth of psychrotrophs, lactic acid bacteria and the total number of viable bacteria compared to the control group during storage (P < 0.05). The rhubarb juice-based marinade significantly delayed the increase in spoilage microorganisms and oxidation parameters compared to the control fillets (P < 0.05). No differences were found between the control and treatment groups in terms of sensory evaluation (P > 0.05). In conclusion, the results show that the juice of rhubarb juice contains a variety of organic acids, polyphenolic compounds and volatiles that contribute to antioxidant capacity and antimicrobial activity. In addition, the use of rhubarb juice as a marinating liquid delayed the oxidation of proteins and lipids, the growth of spoilage microorganisms and improved microbial safety by inhibiting foodborne pathogens in the chicken breast fillets.
Keywords: Bioactive compounds; Chicken breast fillets; Cold storage; Foodborne pathogens; Rhubarb juice.
Copyright © 2024. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
References
-
- Akdeniz İncili C., Karatepe P., Akgöl M., Tekin A., İncili G.K., Hayaloğlu A.A. Evaluation of homemade fermented pickle juice as a marinade: effects on the microstructure, microbiological, physicochemical, textural properties, and sensory attributes of beef strip loin steaks. Meat Sci. 2023;205 - PubMed
-
- Budiarto R., Ujilestari T., Rumhayati B., Adli D.N., Hudaya M.F., Sitaresmi P.I.…Sholikin M.M. Meta-analysis of citrus-derived additives on chicken meat quality and safety: a comprehensive evaluation of acceptability, physicochemical properties, and microbial contamination. Poultry Sci. 2024 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ceylan S., Çetin S., Camadan Y., Saral O., Ozsen O., Tutus A. Antibacterial and antioxidant activities of traditional medicinal plants from the Erzurum region of Turkey. Ir. J. Med. Sci. 2019;188:1303–1309. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

