Magnitude of undernutrition and determinant factors among adult patients with tuberculosis on follow-up care at public healthcare facilities in South Ethiopia Region: a multicentre cross-sectional study
- PMID: 39732485
- PMCID: PMC11683980
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2024-087986
Magnitude of undernutrition and determinant factors among adult patients with tuberculosis on follow-up care at public healthcare facilities in South Ethiopia Region: a multicentre cross-sectional study
Abstract
Background: Globally, approximately 1.9 million cases of tuberculosis (TB) were attributable to undernutrition. Nearly 19 000 deaths occur annually in Ethiopia due to TB. TB makes undernutrition worse and undernutrition deteriorates the body's defence system thus increasing the chance of developing an active illness. However, there is a dearth of studies regarding undernutrition among adult patients with TB in the study setting.
Objective: This study aimed to assess the magnitude of undernutrition and its associated factors among adult patients with TB in the South Ethiopia Region.
Design: We conducted a multicentre cross-sectional study using structured and pretested questionnaires.
Settings: The study was conducted from 5 August 2022 to 5 September 2022, among adult patients with TB on follow-up care in the South Ethiopia Region.
Participants: Three hundred ninety-eight randomly selected adult patients with TB on follow-up care in public healthcare facilities in the Southern Ethiopia region participated in the study.
Methods: Data were collected using structured and pretested questionnaires. Anthropometric measurements were taken by calibrated instruments. EpiData V.3.1 was used for data entry. Data analysis was done by SPSS V.25. Tables, graphs and texts were used to present descriptive statistics. Variables with a p value <0.25 in bivariable logistic regression were candidates for multivariable logistic regression. A p value <0.05 with a 95% CI was used to declare the statistical significance.
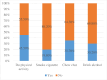
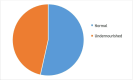
Results: The magnitude of undernutrition was 46.5%, 95% CI 41.5% to 51.5%. Rural residence (adjusted OR (AOR)=3.94, 95% CI 2.52 to 6.17), positive HIV status (AOR=2.65, 95% CI 1.65 to 4.268) and family history of TB (AOR=2.62, 95% CI 1.65 to 4.15) were factors significantly associated with undernutrition.
Conclusion: Our finding indicated that undernutrition among adult patients with TB was relatively high in the study setting compared with similar research reports. Undernutrition was significant among rural residents, positive HIV status and family history of TB. Therefore, we recommend that emphasis should be given to rural residents, positive HIV status and families with a history of patients with TB to decrease its burden.
Keywords: Body Mass Index; Chronic Disease; EPIDEMIOLOGY; NUTRITION & DIETETICS; Tuberculosis.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2024. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
References
-
- WHO . Geneva: World Health Organization; 2023. Global tuberculosis report 2023.https://www.who.int/teams/global-tuberculosis-programme/tb-reports/globa... Available.
-
- WHO . Geneva: World Health Organization; 2022. Global tuberculosis report 2022.https://www.who.int/teams/global-tuberculosis-programme/tb-reports/globa... Available.
-
- WHO . Geneva: World Health Organization; 2023. The global health observatory.https://www.who.int/data/gho Available.
-
- Minister of Health E Sixteenth national tuberculosis research conference. 2022 https://www.moh.gov.et/en/node/331?language_content_entity=en Available.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
