A cross-sectional study assessing customers' perception, satisfaction, and attitude toward e-pharmacy services in Saudi Arabia
- PMID: 39732707
- PMCID: PMC11681715
- DOI: 10.1186/s12913-024-12174-7
A cross-sectional study assessing customers' perception, satisfaction, and attitude toward e-pharmacy services in Saudi Arabia
Abstract
Background: Electronic pharmacy (e-pharmacy) services are growing rapidly, offering increased accessibility, privacy, and value. Understanding e-pharmacy customer satisfaction, attitudes, and perceptions in Saudi Arabia is crucial for improving the services and enhancing health outcomes. This study aims to examine customers' perceptions, preferences, satisfaction, and experiences with electronic pharmacy services, including community pharmacy e-commerce.
Methods: A quantitative cross-sectional design was utilized and conducted in Saudi Arabia. A self-administered online questionnaire was distributed via social media, and convenience sampling was used to collect data from December 2022 to January 2023. The questionnaire was adapted from validated academic questionnaires and consisted of five sections. The online form data was retrieved and analyzed using the IBM SPSS Statistics program.
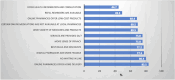
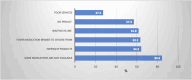
Results: The sample comprised 351 respondents, most of whom were Saudi citizens (90.3%), aged 41-60 years (36.5%), and non-healthcare professionals (35%). Of the participants, 256 (72.93%) were aware of e-pharmacies. Younger participants and those with higher education levels were more aware of e-pharmacies (p < 0.05), with no significant effect of gender or nationality on awareness. Positive perceptions of e-pharmacies exist, but there is limited knowledge about individualized care services (61.8% uncertain). Of the participants, 134 (38.17%) had never used e-pharmacies, and only 24.2% preferred buying medications online, while 75.8% favored physical pharmacies. On a Likert Scale, participants reported moderate levels of satisfaction with e-pharmacies' values/prices and delivery speeds. Many e-pharmacy customers had a positive experience (only 1.1% negative). The findings reveal that service quality, product availability, perceived value, and price could be the potential factors that affect customer satisfaction. Moreover, these factors, along with the provision of personalized care, could shape customers' attitudes toward and perceptions of e-pharmacy.
Conclusions: There is potential for development in e-pharmacy services as seen by the persistence of a preference for traditional pharmacies despite moderate satisfaction ratings. To increase customer satisfaction in Saudi Arabia, we recommend improving personalized care services by raising awareness about e-pharmacy benefits to improve customer satisfaction and adoption.
Keywords: Attitudes; Customer satisfaction; E-pharmacy; Perceptions; Saudi Arabia.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Before enrolment in the study, each participant provided written informed consent. The questionnaires were completed anonymously, and the data was kept strictly confidential. There was no known risk to the study participants. The Research Ethics Committee at King Khalid University granted Institutional Ethical approval (E.C.M. #2022–3115) before the study. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Coherent Market Insights. Global ePharmacy market to reach US$ 244.0 billion by 2027 – Coherent Market Insights. 2020. https://www.coherentmarketinsights.com/press-release/e-pharmacy-market-t.... Accessed 26 Sep 2022.
-
- Sonawane SR, Mahajan VC. Has the outbreak of the Coronavirus pandemic impacted the online pharmacy in Serving the nation or capitalization of business opportunities in India? BVIMSR Journal of Management Research. 2020;12:94–101.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources