Mechanism of activation of TLR4/NF-κB/NLRP3 signaling pathway induced by heat stress disrupting the filtration barrier in broiler
- PMID: 39732713
- PMCID: PMC11681645
- DOI: 10.1186/s12917-024-04411-2
Mechanism of activation of TLR4/NF-κB/NLRP3 signaling pathway induced by heat stress disrupting the filtration barrier in broiler
Abstract
Background: High-temperature environment can cause acute kidney injury affecting renal filtration function. To study the mechanism of renal injury caused by heat stress through activates TLR4/NF-κB/NLRP3 signaling pathway by disrupting the filtration barrier in broiler chickens. The temperature of broilers in the TN group was maintained at 23 ± 1 °C, and the HS group temperature was maintained at 35 ± 1℃ from the age of 21 days, and the high temperature was 10 h per day, and one broiler from each replicate group at the age of 35 and 42 days was selected for blood sampling, respectively.
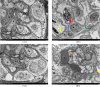
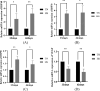
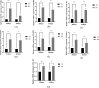
Results: The ELISA results demonstrated that in comparison to the TN group, serum CORT content of broilers in the HS group was all remarkably elevated (P < 0.01); the levels of IL-6 and TNF-α in the serum were remarkably elevated (P < 0.05 or P < 0.01); serum CAT and SOD activities were all remarkably reduced (P < 0.05 or P < 0.01), and serum LDH activity and MDA content were all remarkably decreased (P < 0.05); serum BUN and CRE levels were remarkably elevated (P < 0.01). Pathological sections and transmission electron microscopy demonstrated that the structure of the renal filtration barrier in the HS group damaged gradually with the prolongation of heat stress in comparison to the TN group, but the damage was reduced at 42 days of age; the levels of TLR4, MyD88, NF-κB, NF-κB-p65, NLRP3, caspase-1 and IL-1β mRNAs were all up-regulated (P < 0.05 or P < 0.01) in renal tissues of the HS group, indicating that heat stress caused damage to the morphological structure and function of the renal filtration barrier and that TLR4/NF-κB/NLRP3 pathway was also affected by heat stress, leading to increased activity (P < 0.05 or P < 0.01).
Conclusions: It demonstrated that heat stress caused detrimental effects on both the morphological structure and function of the renal filtration barrier, and the initiation of the TLR4/NF-κB/NLRP3 signaling pathway exacerbated the inflammatory damage, leading to increased thermal damage to renal tissues and glomerular filtration barriers; however, with the prolongation of heat stress, broilers gradually developed heat tolerance, and the damage to the renal tissues and filtration barriers triggered by heat stress was mitigated.
Keywords: Antioxidant capacity; Broiler; Heat shock protein; Heat stress; Renal filtration barrier; TLR4/NF-κB/NLRP3.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: All animals work was adhered the fundamental principles of Basel Declaration and the ethical guidelines of International Council for Laboratory Animal Science (ICLAS). All experimental animals in this study were approved by the Ethics Committee of Henan University of Science and Technology. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Chronic heat stress promotes liver inflammation in broilers via enhancing NF-κB and NLRP3 signaling pathway.BMC Vet Res. 2022 Jul 23;18(1):289. doi: 10.1186/s12917-022-03388-0. BMC Vet Res. 2022. PMID: 35871002 Free PMC article.
-
[Curcumin alleviates nuclear factor-κB/NOD-like receptor protein 3 mediated renal injury caused by acute respiratory distress syndrome through reducing mitochondrial oxidative stress].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2023 Apr;35(4):393-397. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn121430-20230414-00667. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2023. PMID: 37308195 Chinese.
-
Atorvastatin inhibits renal inflammatory response induced by calcium oxalate crystals via inhibiting the activation of TLR4/NF-κB and NLRP3 inflammasome.IUBMB Life. 2020 May;72(5):1065-1074. doi: 10.1002/iub.2250. Epub 2020 Feb 21. IUBMB Life. 2020. PMID: 32083808
-
[Acacetin protects rats from cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury by regulating TLR4/NLRP3 signaling pathway].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2023 Nov;48(22):6107-6114. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20230719.401. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2023. PMID: 38114218 Chinese.
-
The involvement of oxidative stress and the TLR4/NF-κB/NLRP3 pathway in acute lung injury induced by high-altitude hypoxia.Immunobiology. 2024 May;229(3):152809. doi: 10.1016/j.imbio.2024.152809. Epub 2024 May 17. Immunobiology. 2024. PMID: 38788361
References
-
- Wei L, Wang XF, He SJ, Liu DY. The effects of feed additions of bile acids and vitamin E on growth performance and liver and kidney functions of chronically heat-stressed broilers. J Anhui Inst Sci Technol. 2019;33(06):17–22.
-
- Shen P, Shi QM, Gao GP, et al. Histological observation of lymphocytes in the small intestinal epithelium of heat-stressed egg-laying hens treated with Chinese herbs. J Hebei Inst Sci Technol. 2012;26(04):54–7.
-
- Hao SQ, Liu CY, Huang SC, et al. Determination of blood endotoxin and kidney injury indexes in heat-stressed broilers. Progress Anim Med. 2014;35(03):83–6.
-
- Zhang BH, Ye M, Pan ZY, An LL, Zhao ZH, Liu WC. The effects of heat stress on broiler performance. Poult Sci. 2019;05:50–4.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

