Decoding of pain during heel lancing in human neonates with EEG signal and machine learning approach
- PMID: 39732802
- PMCID: PMC11682341
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-82631-0
Decoding of pain during heel lancing in human neonates with EEG signal and machine learning approach
Abstract
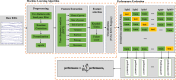
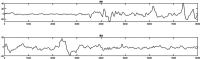
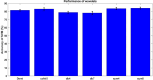
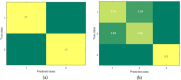
Currently, pain assessment using electroencephalogram signals and machine learning methods in clinical studies is of great importance, especially for those who cannot express their pain. Since newborns are among the high-risk group and always experience pain at the beginning of birth, in this research, the severity of newborns has been investigated and evaluated. Other studies related to the annoyance of newborns have used the EEG signal of newborns alone; therefore, in this study, the intensity of newborn pain was measured using the electroencephalogram signal of 107 infants who were stimulated by the heel lance in three levels: no pain, low pain and moderate pain were recorded as a single trial and evaluated. The support vector machine (SVM), K-Nearest Neighbors (KNN) and Ensemble bagging classifiers were trained using the K-fold cross-validation method and features of the brain's time-frequency domain. The results were obtained with accuracies of 72.8 ± 2, 84.4 ± 1.3 and 82.9 ± 1.6%, respectively. Also, in examining the problem of distinguishing pain and no pain, the electroencephalogram signal of 74 infants was evaluated, and similar to the three-class mode, with the 10-fold validation method, we reached the highest accuracy of 100% in Bagging classifier and 98.6 ± 0.1 accuracy in KNN and SVM classifiers.
Keywords: EEG signals; Human neonates; Pain Decoding.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- van der Vaart, M. L. Multimodal Assessment of Neonatal pain (University of Oxford, 2022).
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

