VPS28 regulates triglyceride synthesis via ubiquitination in bovine mammary epithelial cells
- PMID: 39732879
- PMCID: PMC11682384
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-82774-0
VPS28 regulates triglyceride synthesis via ubiquitination in bovine mammary epithelial cells
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: VPS28 regulates triglyceride synthesis via ubiquitination in bovine mammary epithelial cells.Sci Rep. 2025 May 1;15(1):15300. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-98482-2. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40312432 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
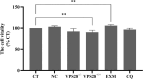
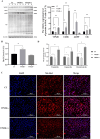
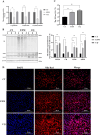
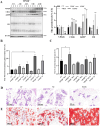
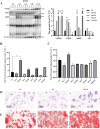
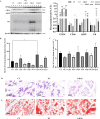
VPS28 (vacuolar protein sorting 28) is a subunit of the endosomal sorting complexes required for transport (ESCRTs) and is involved in ubiquitination. Ubiquitination is a critical system for protein degradation in eukaryotes. Considering the recent findings on the role of ubiquitination in the regulation of lipid metabolism, we hypothesized that VPS28 might affect the expression of genes involved in milk fat synthesis. To test this hypothesis, we modulated VPS28 expression in the bovine mammary epithelial cell line (MAC-T) and measured the effects on triglyceride (TG) synthesis using lentivirus-mediated techniques. The results showed that VPS28 knockdown significantly upregulated the levels of the fatty acid transporter CD36 molecule (CD36) and adipose differentiation-related protein (ADFP), leading to increased TG and fatty acid production, along with elevated ubiquitin (UB) levels, while reducing proteasome activity. In contrast, VPS28 overexpression increased CD36 levels while not significantly affecting ADFP or TG levels, with a trend toward reduced lipid droplets and increased UB expression and proteasome activity. In addition, inhibition of the ubiquitin-proteasome system and the endosomal-lysosomal pathway using epoxomicin and chloroquine, respectively, further increased CD36, ADFP, and TG levels, thereby enhancing cell viability. These in vitro findings were validated in vivo in a mouse model, where VPS28 knockdown increased mammary CD36, ADFP, UB expression, TG content, and lipid droplets without pathological changes in mammary tissue or blood TG alterations. These results confirm the pivotal role of VPS28 in regulating TG synthesis via the ubiquitination pathway, offering novel insights into the molecular mechanisms of milk fat production in a bovine cell model.
Keywords: MAC-T cells; Mouse model; Triglyceride; Ubiquitination; VPS28.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Schulman, B. A. & Harper, J. W. Host ubiquitin protein tags lipid to fight bacteria. Nature594(7861), 28–29 (2021). - PubMed
-
- Xu, G. et al. Post-translational regulation of adipose differentiation-related protein by the ubiquitin/proteasome pathway. J. Biol. Chem.280(52), 42841–42847 (2005). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

