Diagnostic value of combined maternal cardiac work and fetoplacental circulation parameters in detecting fetal intrauterine hypoxia in preeclamptic women
- PMID: 39732899
- PMCID: PMC11682035
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-82545-x
Diagnostic value of combined maternal cardiac work and fetoplacental circulation parameters in detecting fetal intrauterine hypoxia in preeclamptic women
Abstract
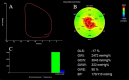
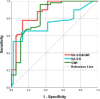
To investigate the correlation between fetoplacental circulation and maternal left ventricular myocardial work (MW) parameters in patients with preeclampsia (PE) and the prediction of fetal hypoxia. Seventy-eight PE patients (PE group) were assigned to intrauterine-hypoxia (27) and non-intrauterine-hypoxia (51) groups, and 45 healthy pregnant women were controls. The receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve evaluated the diagnostic efficacy of each parameter for fetal intrauterine hypoxia. Relative to the controls and the non-intrauterine-hypoxia group, the umbilical artery (UA) S/D, PI, and RI, as well as the global work index (GWI), global effective work, and global ineffective work, increased in the PE group and intrauterine-hypoxia group (P < 0.05), respectively, while the cerebroplacental ratio (CPR) and global work efficiency decreased (P < 0.05). Relative to the controls group, the middle cerebral artery S/D, PI, and RI decreased in the PE group (P < 0.05). Correlation analysis showed that the fetoplacental circulation parameters were correlated with MW parameters (P < 0.05), and CPR achieved the highest correlation. ROC curves showed that UA-S/D, combined with GWI, produced the highest predictive value for fetal hypoxia in PE patients. There was a linear correlation between MW parameters and fetoplacental parameters, and CPR showed the highest correlation with MW. UA-S/D, combined with GWI, exhibited optimal diagnostic efficacy in predicting fetal intrauterine hypoxia in PE patients.
Keywords: Fetal intrauterine hypoxia; Fetoplacental circulation; Myocardial work; Preeclampsia.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

