Metagenomic next-generation sequencing and galactomannan testing for the diagnosis of invasive pulmonary aspergillosis
- PMID: 39732910
- PMCID: PMC11682328
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-82806-9
Metagenomic next-generation sequencing and galactomannan testing for the diagnosis of invasive pulmonary aspergillosis
Abstract
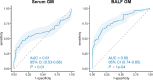
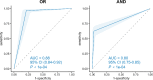
To evaluate the diagnostic value of metagenomic next-generation sequencing (mNGS) and galactomannan (GM) testing in invasive pulmonary aspergillosis (IPA) and to compare mNGS with other diagnostic approaches (serum/bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF)-GM and conventional microbiological tests (CMTs) including sputum smears and culture, BALF fungal culture, and bronchial brushing). In all, 237 patients were enrolled in this retrospective study, including 120 patients with IPA and 117 with non-IPA pulmonary infections treated at Henan Provincial People's Hospital between June 2021 and February 2024. The diagnostic performance of mNGS was compared to conventional diagnostic methods including serum GM, BALF-GM, sputum smear microscopy, sputum culture, bronchial brushings, and BALF culture. The proportion of patients with underlying diseases was significantly higher in the IPA group than in the non-IPA group (P < 0.05). Compared to conventional diagnostic methods for IPA, mNGS showed higher diagnostic efficacy, with a sensitivity of 92.5% and a specificity of 94.02%. The area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC) for BALF-GM for diagnosing IPA was 0.8, with an optimal cutoff value of 0.546, sensitivity of 66.7%, and specificity of 82.1%. The combination of mNGS and BALF-GM testing further improved diagnostic performance (sensitivity of 96.67% and specificity of 78.63%). mNGS testing has excellent diagnostic efficacy for IPA, which is further enhanced by combining it with BALF-GM testing. This approach has considerable potential for the early diagnosis and targeted treatment of IPA.
Keywords: Bronchoalveolar lavage fluid; Diagnostic performance; Galactomannan; Invasive pulmonary aspergillosis; Metagenomic next-generation sequencing.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: This study was approved by the Medical Ethics Committee of Henan provincial People’s Hospital (Approve No: 2023151). All methods were carried out in accordance with the declaration of Helsinki. Written informed consent was obtained from all subjects. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Clinical utility of metagenomic next-generation sequencing in the diagnosis of invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease patients in the intensive care unit.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024 Jul 12;14:1397733. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1397733. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39071167 Free PMC article.
-
The clinical utility of bronchoalveolar lavage fluid metagenomic next-generation sequencing in immunocompromised critically ill patients with invasive pulmonary aspergillosis: a multicenter retrospective study.Microbiol Spectr. 2025 Aug 5;13(8):e0058425. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.00584-25. Epub 2025 Jun 12. Microbiol Spectr. 2025. PMID: 40503829 Free PMC article.
-
Performance of mNGS in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid for the diagnosis of invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in non-neutropenic patients.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023 Oct 31;13:1271853. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2023.1271853. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 38029249 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic value of bronchoalveolar lavage fluid galactomannan assay for invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in adults: A meta-analysis.J Clin Pharm Ther. 2022 Dec;47(12):1913-1922. doi: 10.1111/jcpt.13792. Epub 2022 Nov 2. J Clin Pharm Ther. 2022. PMID: 36324286 Review.
-
Performance of existing definitions and tests for the diagnosis of invasive aspergillosis in critically ill, adult patients: A systematic review with qualitative evidence synthesis.J Infect. 2020 Jul;81(1):131-146. doi: 10.1016/j.jinf.2020.03.065. Epub 2020 Apr 21. J Infect. 2020. PMID: 32330523
Cited by
-
Metagenomic sequencing for identification of nontuberculous mycobacteria and other pathogens in patients with mixed infection of the lung.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2025 Jun 19;15:1592216. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2025.1592216. eCollection 2025. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40612390 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Denning, D. W. Global incidence and mortality of severe fungal disease. Lancet Infect. Dis.24, e428–e438 (2024). - PubMed
-
- Douglas, A. P. et al. Consensus guidelines for the diagnosis and management of invasive aspergillosis, 2021. Intern. Med. J.51 (Suppl 7), 143–176 (2021). - PubMed
-
- [Expert consensus on the. Diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary aspergillosis in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease]. Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi. 47, 604–622 (2024). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- Zhengzhou University, 518-23240003/518-23240004/This study was supported by the Zhengzhou Collaborative Innovation Major Project
- Zhengzhou University, 518-23240003/518-23240004/This study was supported by the Zhengzhou Collaborative Innovation Major Project
- Zhengzhou University, 518-23240003/518-23240004/This study was supported by the Zhengzhou Collaborative Innovation Major Project
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

