CHD1L accelated the progression of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma via promoting PI3K/PD-L1 signaling pathway induced M2 polarization of TAMs
- PMID: 39732937
- PMCID: PMC11682224
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-82594-2
CHD1L accelated the progression of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma via promoting PI3K/PD-L1 signaling pathway induced M2 polarization of TAMs
Abstract
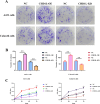
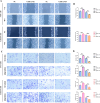
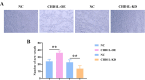
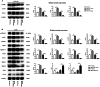
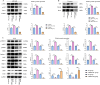
To investigate CHD1L's impacts and molecular processes in hypoxic cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. Monoclonal proliferation assays and CCK-8 were used to detect the proliferation capacity of A431 cells and Colon16 cells; wound healing experiments and Transwell assays were used to examine the migration and invasion capacity of A431 cells and Colon16 cells; angiogenesis experiments were conducted to assess the influence of A431 cells on angiogenesis; a nude mouse tumor xenograft experiment and HE staining were utilized to evaluate the impact of CHD1L on the progression of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma; western blot analysis was performed to detect the expression of p-PI3K, p-AKT, and PD-L1 in A431 cells, as well as CD9, TSG101, PD-L1 in exosomes, and CD206, Arginase-1, iNOS, IL-1β, p-AKT, p-mTOR, VEGF, COX-2, MMP2, MMP9, p-ERK1/2 in tumor-associated macrophages. Under hypoxic conditions, CHD1L promoted the proliferation, migration, invasion, and angiogenesis of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. Furthermore, CHD1L facilitated the progression of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. CHD1L also increased the relative protein expression of p-PI3K, p-AKT, and PD-L1 in A431 cells, as well as CD9, TSG101, PD-L1 in exosomes, CD206, Arginase-1, p-AKT, p-mTOR, VEGF, COX-2, MMP2, MMP9, and p-ERK1/2 in tumor-associated macrophages, while inhibiting the relative protein expression of iNOS and IL-1β. Under hypoxic conditions, CHD1L can promote the proliferation and migration of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma.
Keywords: CHD1L; Cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma; Hypoxia; Tumor-associated macrophages.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Ethics approval: Animal experiments were performed according to the guidelines laid down by the Laboratory Animal Ethical and Welfare Committee of Affiliated Hospital of Hebei Engineering University (IACUC-Hebeu-2023-0019).
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effect of chromodomain helicase/ATPase DNA binding protein 1-like gene on the invasion and metastasis of tongue squamous cell carcinoma CAL27 cells.Hua Xi Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2021 Feb 1;39(1):81-87. doi: 10.7518/hxkq.2021.01.012. Hua Xi Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2021. PMID: 33723941 Free PMC article. Chinese, English.
-
Bu Fei Decoction attenuates the tumor associated macrophage stimulated proliferation, migration, invasion and immunosuppression of non-small cell lung cancer, partially via IL-10 and PD-L1 regulation.Int J Oncol. 2017 Jul;51(1):25-38. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2017.4014. Epub 2017 May 19. Int J Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28534943 Free PMC article.
-
lncRNA EZR‑AS1 knockdown represses proliferation, migration and invasion of cSCC via the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway.Mol Med Rep. 2021 Jan;23(1):76. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2020.11714. Epub 2020 Nov 25. Mol Med Rep. 2021. PMID: 33236153 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of PTEN inactivation and PD-1/PD-L1 activation in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.Mol Biol Rep. 2022 Jul;49(7):6633-6645. doi: 10.1007/s11033-022-07246-y. Epub 2022 Mar 17. Mol Biol Rep. 2022. PMID: 35301651 Review.
-
CHD1L in cancer and beyond: structure, oncogenic functions, and therapeutic potential.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2025 May 30;44(1):167. doi: 10.1186/s13046-025-03428-1. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2025. PMID: 40442742 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- McLean, L. S. et al. A phase II study of tarloxotinib (a hypoxia activated prodrug of a pan-erb tyrosine kinase inhibitor) in patients with recurrent or metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck or skin. Invest. New Drugs40(4), 782–788 (2022). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

